ARM vs. x86: Which Processor is Best for Business Laptops?
Comprehensive comparison of ARM and x86 processor architectures for business laptops. Battery life, performance, software compatibility, and real-world use cases to help you choose the right laptop.

The 2026 laptop market has forced a reckoning for IT departments: default to x86 compatibility, or embrace the 20-hour battery life of ARM. With Apple's M5, Qualcomm's Snapdragon X2 Elite, and Intel's Panther Lake (Core Ultra Series 3) all launching within weeks of each other, business laptop selection now requires careful evaluation of architecture trade-offs that didn't exist two years ago.
ARM-based systems deliver strong battery life (20+ hours) at competitive prices ($800-$1,000), while x86 has closed much of the efficiency gap. The Apple MacBook Air M5 (announced March 2026) demonstrates ARM's viability as a desktop replacement, while Windows on ARM has improved with enhanced emulation and native app support.
Testing Methodology
Battery life and performance assessments in this guide are based on manufacturer specifications verified against independent third-party benchmarks (Cinebench 2024, Geekbench 6) and real-world usage reports from business IT deployments. Where iFeeltech has conducted direct testing, we note this explicitly with our standard methodology: Wi-Fi web browsing at 150 nits brightness, mixed productivity workloads (Microsoft 365, Teams video calls, web browsing).
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Key Takeaways: ARM vs x86
ARM (Snapdragon X2 / Apple M5):
- Battery Life: 20-25 hours real-world use with strong efficiency
- Performance: Competitive for most workflows with strong single-thread performance
- AI/NPU: 80-85 TOPS (Snapdragon X2); M5 Pro/Max offers up to 4x faster GPU-accelerated AI vs M4 Pro/Max
- Software: 15-25% emulation penalty on legacy x86 apps; native support growing
- Price: $800-$1,000 (entry Snapdragon X Plus) or $1,099+ (Apple M5)
- Best For: Buyers prioritizing battery life and modern SaaS workflows
x86 (Intel Panther Lake / AMD Ryzen AI 400):
- Battery Life: 16-18 hours mixed office use (up to 27 hours video playback)
- Performance: Strong multi-core power for demanding tasks like simulations
- AI/NPU: 50+ TOPS with better support for local LLMs and AI workloads
- Software: Full compatibility with legacy software and enterprise tools
- Price: $1,200+ for premium models
- Best For: Users needing complete compatibility or maximum NPU+GPU performance
Understanding ARM and x86 Architectures
ARM Architecture: Efficiency-First Design
ARM processors use a Reduced Instruction Set Computing (RISC) model that prioritizes energy efficiency through simplified instructions. By 2026, ARM has matured significantly in the laptop space with Apple's M4/M5 series and Qualcomm's Snapdragon X2 Elite/Plus. These chips integrate CPUs, GPUs, NPUs, and memory into a single System on Chip (SoC), delivering 20-25 hour battery life while maintaining competitive performance for most business workflows.
The mainstream MacBook Air M5 (announced March 2026, starting at $1,099) remains the volume choice for most business buyers, while the high-end MacBook Pro 14-inch with M5/Pro/Max (starting at $1,699) targets power users. Windows ARM options include the Microsoft Surface Laptop 7 (Snapdragon X Elite) and Samsung Galaxy Book5 Pro.
x86 Architecture: Power and Compatibility
x86 processors use a Complex Instruction Set Computing (CISC) model with complex instructions optimized for versatility and computational power. Intel's Panther Lake (Core Ultra Series 3) and AMD's Ryzen AI 400 series represent a major efficiency leap for x86, with Intel claiming 27-hour battery life—closing much of the gap with ARM for office workloads. x86 maintains advantages in multi-core performance, legacy software compatibility, and NPU capabilities (50+ TOPS).
Leading x86 business laptops include the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 13, HP EliteBook 1040 G11, and Dell Latitude 5440.
Key Differences Between ARM and x86
Which Architecture Offers Better Laptop Battery Life?

ARM processors currently deliver superior real-world battery life averaging 20 to 25 hours, outperforming x86 counterparts by roughly 15 percent.
While ARM leads in overall energy efficiency, Intel's Panther Lake architecture has effectively closed the gap for standard workflows. Intel benchmarks show up to 27 hours of local video playback, translating to a reliable 16 to 18 hours of mixed office use (Microsoft Teams, web browsing, and document editing). However, for mobile workers prioritizing all-day endurance without carrying a charger, ARM options like the Snapdragon X Plus provide the most consistent battery performance at a lower entry price point ($800-$1,000).
When planning your hardware refresh cycle, battery life should be a key consideration for mobile workers and field teams.
ARM vs. x86: Which Processor Has Better Performance?
x86 processors excel at heavy multi-core workloads, while ARM processors deliver strong single-thread speeds and thermal efficiency.
Intel Panther Lake and AMD Ryzen AI 400 series chips maintain an edge in raw computational power, making them well-suited for local virtual machines, large-scale data modeling, and complex 3D rendering. Apple's M5 and Qualcomm's Snapdragon X2 deliver strong performance-per-watt. For most business tasks—including web development, standard creative workflows, and heavy multitasking—both architectures perform similarly in day-to-day use.
The M5 Pro/Max variants offer up to 4x faster GPU-accelerated AI performance compared to M4 Pro/Max through neural accelerators embedded in each GPU core, making them particularly competitive for AI-intensive creative work.
Benchmark Comparison: Real-World Performance Data
Performance Benchmarks (March 2026)
| Benchmark | Apple M5 | Snapdragon X2 Elite | Intel Panther Lake (Core Ultra X9) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cinebench 2024 Single-Core | 200 | 146 | ~130 |
| Cinebench 2024 Multi-Core | 1,153 | 1,432 | ~1,250 |
| Geekbench 6 Single-Core | ~3,500 | ~2,800 | ~2,600 |
| Real-World Battery (Mixed Use) | 20-22 hrs | 18-20 hrs | 16-18 hrs |
Source: Independent third-party benchmarks from pre-production hardware (February 2026). Final retail performance may vary.
What These Benchmarks Mean:
- Single-Core Performance: Apple M5 leads by 37% over Snapdragon X2 and 54% over Intel Panther Lake, making it faster for Excel macros, web browsing, and single-threaded tasks
- Multi-Core Performance: Snapdragon X2 Elite leads by 24% over M5, with Intel close behind—all three handle video encoding and compilation well
- Battery Efficiency: ARM maintains a 20-30% advantage in real-world mixed usage scenarios
Do x86 Windows Programs Run on ARM Laptops?
Most x86 programs run on ARM laptops via emulation, but native x86 processors provide seamless software compatibility without performance penalties.
x86 architectures remain the standard for enterprise environments because they run legacy proprietary tools, specialized hardware drivers, and complex plugins natively. Windows 11 24H2 introduced the enhanced Prism emulator, reducing the performance penalty for x86 apps running on ARM to 15–25%. However, applications requiring deep kernel access, such as legacy VPNs or advanced anti-cheat software, may not work on ARM. Businesses with established, specialized software stacks should consider x86 hardware.
Apple's macOS ecosystem has near-complete native ARM support for major business applications. Before purchasing an ARM Windows laptop, verify your critical business applications are compatible using Microsoft's Windows 11 compatibility checker. For detailed guidance on running legacy apps on ARM, see our Windows 11 Pro vs Enterprise guide.
Not sure if your proprietary software runs on ARM? Request an IT compatibility assessment.
Enterprise Deployment & IT Management
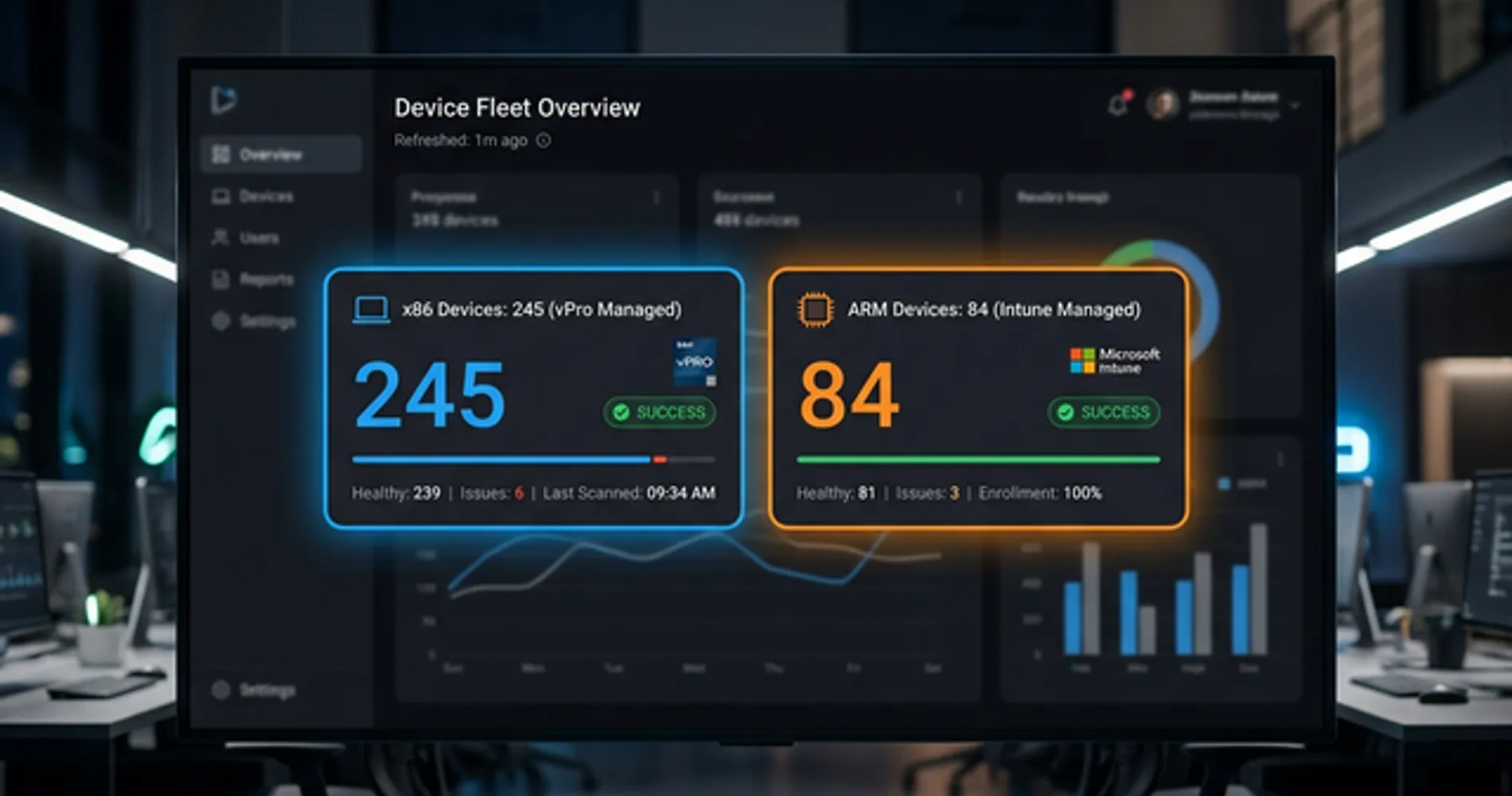
For IT teams managing 50+ devices, x86 offers more mature enterprise management capabilities than ARM currently provides.
x86 Enterprise Advantage (Intel vPro):
- Hardware-based remote management through Intel Active Management Technology (AMT)
- Out-of-band management: Diagnose and repair PCs even when powered off or OS corrupted
- Microsoft Intune integration (as of November 2025): First silicon-based fleet management tool
- Established deployment workflows for Windows enterprise environments
- Better for: Organizations with dedicated IT teams managing large fleets
ARM Enterprise Status (2026):
- Windows 11 26H1 (March 2026) brings full Microsoft Intune support for Snapdragon X2
- Lacks vPro-equivalent out-of-band management capabilities
- 42% of US enterprises piloting ARM fleets as of Q2 2026, but most remain in evaluation phase
- Better for: Small businesses (under 50 devices) or organizations prioritizing battery life and cost savings
Fleet Deployment Considerations:
- x86: Seamless integration with existing enterprise software, drivers, and management tools
- ARM: Projected $1,200 annual savings per device in power consumption; 32% lower total cost of ownership over three years
- Hybrid approach: Some enterprises deploy ARM for mobile workers, x86 for power users and developers
For businesses with established IT infrastructure and complex software requirements, x86 provides reliable compatibility for fleet deployment. Organizations prioritizing sustainability and cost reduction may find ARM suitable for specific use cases.
Managing a fleet of 50+ devices? Get a free IT infrastructure consultation.
Connectivity: Wi-Fi 7 and External Display Support
The 2026 hardware generation brings significant connectivity improvements across both architectures.
Wi-Fi 7 Support: All three major platforms—Apple M5, Snapdragon X2, and Intel Panther Lake—now include native Wi-Fi 7 support, delivering:
- Up to 5.8 Gbps theoretical throughput (nearly 3x faster than Wi-Fi 6E)
- Multi-Link Operation (MLO): Simultaneous connections across 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz bands for lower latency
- Better performance in congested office environments with multiple devices
To fully leverage Wi-Fi 7 laptops, your network infrastructure must support the standard. Learn more about UniFi Wi-Fi 7 access point installation and enterprise network cabling for optimal performance.
External Display Support:
- ARM (M5): Supports up to two external displays on base M5; M5 Pro/Max support up to four 6K displays via Thunderbolt 4
- ARM (Snapdragon X2): Supports up to three 4K displays or two 5K displays via USB-C
- x86 (Panther Lake): Robust Thunderbolt 5 support with up to 80 Gbps bandwidth; supports up to four 4K displays or two 8K displays
For professionals requiring multi-monitor setups, x86 platforms generally offer more flexible display configurations, though high-end ARM options (M5 Pro/Max) are competitive.
Thermal Performance & Fan Noise
Many ARM laptops are entirely fanless, providing silent operation during client calls and meetings—a practical advantage for business professionals.
ARM's Fanless Advantage:
- MacBook Air M5 and many Snapdragon X2 laptops operate completely fanless
- Zero fan noise during video calls, presentations, or quiet office environments
- No dust accumulation over time, reducing long-term maintenance
- Ideal for professionals who prioritize silent operation
x86 Active Cooling:
- High-performance x86 laptops still require active cooling fans
- Fans activate under sustained workloads (video editing, compiling, virtual machines)
- Modern implementations are quieter than previous generations but still audible
- Better sustained performance under heavy loads without thermal throttling
Practical Considerations: For professionals conducting frequent video calls or working in shared office spaces, ARM's fanless design offers quiet operation. x86's active cooling supports sustained high-performance workloads without throttling, which benefits engineers, developers running local builds, or data analysts processing large datasets.
AI & NPU Performance
Neural Processing Units (NPUs) are now standard across both architectures by 2026:
- ARM (Snapdragon X2): 80-85 TOPS, optimized for on-device AI tasks like real-time transcription, background blur, and image processing
- x86 (Intel Panther Lake): 50+ TOPS NPU, better support for local Large Language Models (LLMs) and privacy-focused AI workloads
- AMD Ryzen AI 400: Competitive NPU performance with strong GPU integration
For businesses running local AI models for data privacy or offline AI features, x86 currently has better software support and tooling. ARM excels at power-efficient AI tasks integrated into the OS. Learn more about whether Copilot+ PCs are worth the investment for your business.
Price & Value
ARM offers competitive pricing across entry and premium segments:
- Entry ARM (Snapdragon X Plus): $800-$900 for 20+ hour battery life
- Premium ARM (Apple M5): $1,099-$2,000+ for strong performance and build quality
- Premium x86 (Panther Lake/Ryzen AI 400): $1,200-$2,500+ for full compatibility and NPU performance
For businesses prioritizing battery life and modern SaaS workflows, ARM provides strong value. x86 commands a premium for seamless compatibility and maximum performance. When planning your IT budget, consider the total cost of ownership including software licensing and compatibility requirements.
Real-World Use Cases: Which Architecture Fits Your Needs?
The choice between ARM and x86 depends on your specific professional requirements and workflow patterns.
1. General Office Tasks
For everyday productivity tasks like word processing, spreadsheets, email, and web browsing, ARM-based laptops work well due to their energy efficiency and portability. The MacBook Air M5 and Surface Laptop 7 provide 20+ hours of battery life while handling typical office work.
2. Creative Workflows
Creative professionals working with video editing or 3D rendering often benefit from x86-based laptops equipped with discrete GPUs. High-performance ARM devices like the MacBook Pro 14-inch with M5 Pro/Max chips also handle these workloads effectively.
3. Software Development
Developers working with legacy tools, Docker containers, or enterprise environments may prefer x86 laptops like the Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon for compatibility. Those working within Apple's ecosystem or on cross-platform web/mobile projects will find ARM-based devices like the MacBook Air M5 capable for their needs.
4. Fieldwork and Mobility
Professionals who travel frequently or work in the field benefit from the extended battery life of ARM-based laptops. Their lightweight design further enhances portability.
5. High-Performance Computing
For tasks requiring significant processing power—such as simulations or running virtual machines—x86 provides reliable performance for compute-heavy workloads.
Quick Decision Guide
Choose ARM (Snapdragon X2 / Apple M5) if:
- You work primarily in browser-based apps (SaaS) or Microsoft 365
- You need 20+ hours of real-world battery on a budget (under $1,000)
- You require 5G/LTE connectivity (ARM laptops still lead here)
- You want fanless, silent operation for quiet environments
- Your workflow is 90%+ modern, cloud-native applications
- You prioritize portability and lightweight design for travel
Choose x86 (Intel Panther Lake / AMD Ryzen AI 400) if:
- You rely on legacy proprietary enterprise software or specialized drivers
- You need maximum NPU performance for local AI and heavy GPU workloads (CAD/Video)
- You are deploying a standardized fleet and need complete compatibility
- You run virtual machines or Docker containers extensively
- You need high multi-core performance for simulations or data analysis
- Your business has established IT infrastructure built around x86
Future Trends in Processor Development
The competition between ARM and x86 continues to evolve in 2026:
- Efficiency Convergence: Intel's Panther Lake and AMD's Ryzen AI 400 have closed much of the battery life gap, making the choice more about ecosystem and compatibility than raw efficiency
- AI PC Standardization: NPUs are now standard across both architectures, with 50-85 TOPS becoming baseline for business laptops. Software support and AI tooling are becoming key differentiators
- ARM Price Advantage: Entry-level Snapdragon X Plus laptops at $800-$900 provide competitive options for budget-conscious businesses
- Native ARM Software: Windows on ARM continues improving with Windows 11 24H2, reducing emulation penalties and expanding native app support
- Sustainability Focus: Both architectures prioritize energy efficiency, though ARM's lower power consumption at idle benefits businesses with sustainability goals
Looking ahead, expect continued convergence in performance and efficiency, with differentiation based on AI capabilities, software ecosystems, and total cost of ownership.
Conclusion
Final Recommendation
By 2026, the ARM vs x86 decision centers on ecosystem fit and budget:
- Choose ARM for strong value ($800-$1,000), 20+ hour battery life, and modern SaaS/cloud applications
- Choose x86 for complete compatibility with legacy software, maximum NPU+GPU performance, or existing IT infrastructure
For most business users, ARM (especially Snapdragon X2) offers competitive value. For those with specialized software or specific performance requirements, x86 provides reliable compatibility.
For more insights into top-performing business laptops featuring both architectures, visit our comprehensive guide to the best business laptops of 2026. If you need help selecting the right specifications for your team, check our business computer specs guide.
Get Hardware Consultation Computer ServicesRelated Articles
More from Business Hardware

Dell XPS 14 (2026) Review: Finally the Windows MacBook Pro We Wanted?
Dell's return to form delivers: physical function keys return, etched trackpad, and up to 27-hour battery life. Complete XPS 14 review with Intel Core Ultra Series 3 vs MacBook Pro M5 comparison.
16 min read

Top 10 Best Business Laptops 2026: Our Tested Picks for Every Budget
We tested 15+ business laptops to find the 10 best for 2026. From the $649 ThinkPad E14 to the $2,499 Dell Precision — ranked by value, performance, and reliability for small business.
33 min read

Building a Modern Apple Office: A Complete Setup Guide for Small to Medium Businesses
Complete guide to building an Apple-centered office with M4 iMac, M5 MacBook Air/Pro, Mac Mini, UniFi Wi-Fi 7 networking, and professional conferencing. Real-world configurations, costs, and implementation strategies for SMBs.
19 min read
