Small Business Network Setup Guide 2026: The Complete Blueprint
Build a secure, scalable business network in 2026. Complete guide to WiFi 7, cabling costs, UniFi gear, and Zero Trust security for 5-50 users. Updated for Miami businesses.


Key Information
Setting up a small business computer network requires methodical planning of infrastructure, equipment selection, and implementation strategy. This guide covers the complete process from initial assessment to final testing, helping you build a reliable, secure, and scalable network that supports 5-50 employees within current market budgets.
Setting up a computer network for your small business is the backbone of your operations. A properly designed network enables productivity, security, and business growth, while poor planning leads to slow speeds, security holes, and costly re-wiring.
Whether you're establishing your first office, relocating your business, or upgrading existing infrastructure, this guide provides a systematic approach to building professional network infrastructure that will serve your business needs.
Network Planning: Assessment and Requirements
Business Requirements Documentation
Before selecting any equipment, document your network requirements comprehensively. This assessment forms the foundation for all subsequent decisions.
Current State Analysis:
- Number of employees and workstations
- Device types requiring connectivity (computers, phones, tablets, IoT devices)
- Internet usage patterns and bandwidth requirements
- File sharing and collaboration workflows
- Security and compliance obligations
Growth Planning:
- Projected staff growth over 2-3 years
- Plans for additional locations or remote workers
- New applications or systems under consideration
- Budget parameters and implementation timeline
South Florida Business Considerations
For businesses in Miami and surrounding areas, consider hurricane season continuity planning, humidity impacts on equipment selection, and the increasing prevalence of hybrid work arrangements requiring robust remote access capabilities. Coastal Miami Beach offices should prioritize corrosion-resistant equipment and proper environmental sealing to protect against salt air exposure, which can significantly reduce equipment lifespan.
Network Architecture Planning
Wired and Wireless Integration:
Modern small business networks strategically combine wired and wireless connectivity. Wired connections provide maximum reliability and speed for stationary equipment, while wireless infrastructure supports mobile devices and guest access.
For typical 5-25 person offices:
- Wired connections for desktop computers, printers, and servers
- Wireless infrastructure for laptops, tablets, phones, and guest devices
- Strategic wireless access point placement for comprehensive coverage
Network Topology:
Small businesses typically implement a star topology with central switching infrastructure connecting all devices. This approach provides:
- Centralized management and monitoring capabilities
- Simplified troubleshooting and maintenance procedures
- Scalability for future expansion
- Enhanced security control
Core Network Components and Equipment Selection
Essential Infrastructure Components
1. Internet Gateway and Routing
Your gateway device connects internal network infrastructure to the Internet while providing essential services, such as firewall protection, secure remote access, and bandwidth management.
Multi-Gigabit Internet Considerations: In 2026, ISP speeds in Miami (AT&T, Comcast) routinely offer 2Gbps and 5Gbps plans. To fully utilize these speeds, consider gateways that support multi-gigabit WAN ports (2.5GbE or higher).
Options for small businesses include:
- Consumer-grade routers: Appropriate only for very small offices (under 5 users)
- Business-grade routers: Enhanced performance and security features with multi-gigabit support
- Unified Threat Management (UTM) devices: Comprehensive security and management capabilities
- Enterprise-level solutions: Designed for growing businesses with complex requirements
Internet Redundancy: For Miami businesses where connectivity is critical, consider implementing a Dual-WAN setup: a primary fiber line paired with a secondary 5G/LTE backup or cable connection. Modern gateways can handle this failover automatically, minimizing downtime during outages.
UniFi Equipment Recommendations
For most small businesses, the UniFi Dream Machine Pro (approximately $400) or Dream Machine Pro Max ($599) provides substantial value with enterprise-grade features, an intuitive management interface, and expansion capabilities. Learn more in our complete UniFi business network guide.
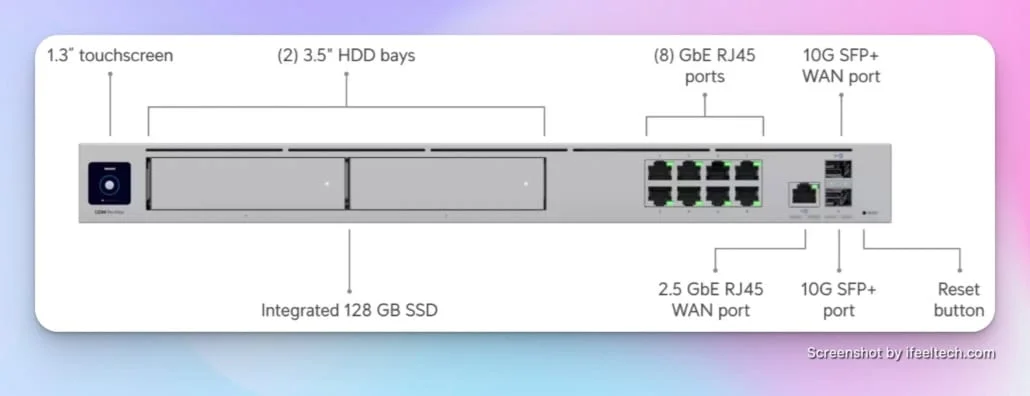
2. Network Switching Infrastructure
Switches connect wired devices and provide the backbone for network infrastructure.
Key selection criteria:
- Port capacity: Plan for 20-30% more ports than current requirements
- Power over Ethernet (PoE): Required for wireless access points, IP phones, and security cameras. See our PoE implementation guide for detailed planning
- Management capabilities: Managed switches offer superior control and monitoring
- Speed requirements: Gigabit connectivity remains standard for most businesses, though 2.5GbE switching is increasingly common for creative and tech businesses in 2026. With WiFi 7 capable of multi-gigabit speeds and ISPs offering 2Gbps+ connections, 2.5GbE switches help avoid potential bottlenecks. Consider 10GbE uplinks for high-performance environments
3. Wireless Access Points
Modern wireless access points connect mobile devices and laptops throughout your facility.
Coverage Planning:
- One access point per 1,500-2,000 square feet for typical office environments
- Strategic placement to minimize interference and optimize coverage
- Consideration of outdoor coverage requirements for parking or patio areas
- Additional capacity planning for high-density areas such as conference rooms
Current Wireless Standards (2026):
WiFi 7 Adoption in 2026: WiFi 7 certified devices are increasingly common on laptops and phones. While WiFi 6E remains a solid choice, WiFi 7 offers improved latency and throughput that benefits video conferencing and cloud-based collaboration. For new deployments, WiFi 7 provides better long-term value.
- WiFi 7 (802.11be) recommended for all new deployments - see UniFi WiFi 7 access points
- WiFi 6E minimum acceptable standard
- Multiple SSID configuration for different user types (employees, guests, IoT devices)
Cabling Infrastructure
Cable Selection Standards:
- Cat6: Sufficient for most small business applications (supports 1 Gbps to 328 feet, 10 Gbps to 165 feet)
- Cat6A: Enhanced specifications for 10GbE applications (supports 10 Gbps to 328 feet at 500 MHz). See our Cat6 vs Cat6A comparison guide for detailed specifications and our best ethernet cable guide for tested product picks
- Fiber optic: Required for longer runs or specialized high-bandwidth applications
Professional Installation Requirements
Structured cabling installation typically requires professional contractors, particularly in commercial buildings where building codes, permits, and compliance standards apply. As of July 2025, current installation costs averaged $120-$344 per wiring run.
Installation Requirements:
- Proper cable management and comprehensive labeling
- Adequate power infrastructure and cooling for equipment
- Physical security for network closets and equipment
- Complete documentation for future maintenance and modifications
Security Foundation and Best Practices
Network Security Implementation
Firewall Configuration:
- Default-deny policies with specific allow rules
- Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- AI Threat Detection: Modern firewalls in 2026 use AI to detect anomalies and identify threats in real-time, analyzing traffic patterns to catch zero-day attacks that signature-based systems miss
- Regular firmware updates and security patches
- Comprehensive logging and network traffic monitoring
Wireless Security Standards:
- WPA3 encryption (minimum WPA2 for legacy device compatibility)
- Strong passphrase policies and regular rotation
- Guest network isolation from business systems
- Regular access credential updates
Access Control Management:
- Network segmentation for different user categories
- Zero Trust & Remote Access: Modern security practices increasingly favor Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) principles over traditional VPNs. ZTNA requires users to verify identity (MFA) before accessing specific applications. For UniFi users, features like 'Teleport' or 'Identity Enterprise' provide secure access with reduced lateral movement risks compared to always-on VPN tunnels. Learn more about network security best practices
- Device authentication and authorization protocols
- Regular access reviews and updates
Backup and Disaster Recovery
Network Configuration Protection:
- Regular automated backups of all network device configurations
- Comprehensive documentation of network topology and settings
- Defined recovery procedures and emergency contact information
- Regular testing of backup and recovery processes
Business Continuity Planning:
- Redundant internet connections where operationally feasible
- Backup power solutions (UPS systems)
- Disaster preparedness planning appropriate for South Florida weather patterns
- Remote work capabilities and secure access infrastructure
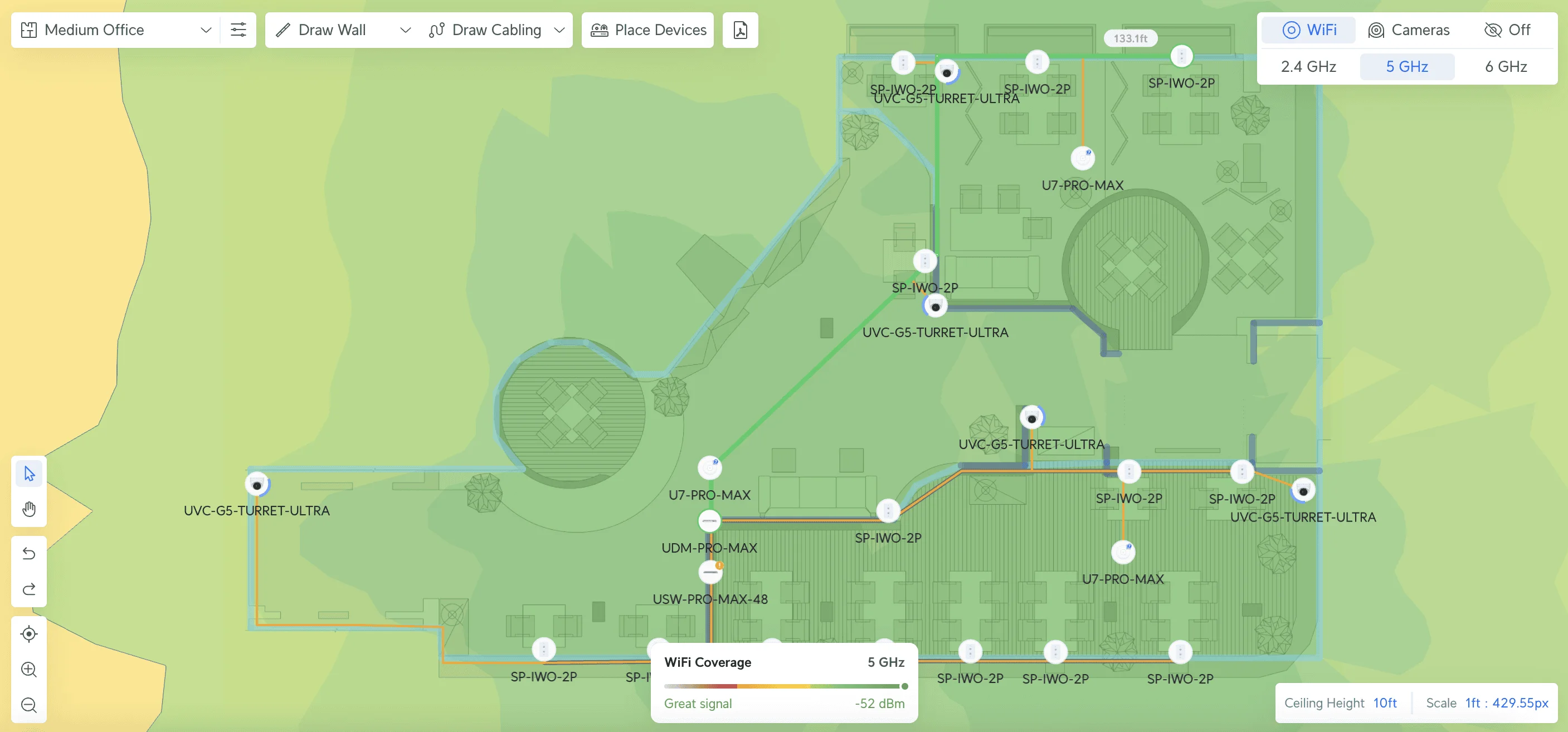
Implementation Strategy and Project Timeline
Successfully implementing a business network requires careful coordination across multiple phases. While some businesses handle this internally, working with experienced professionals can significantly reduce implementation time and avoid costly mistakes.
Phase 1: Planning and Preparation (Weeks 1-3)
Site Assessment and Planning:
- Comprehensive measurement of office space and equipment location identification
- Assessment of existing infrastructure and equipment condition
- Cable routing and access point location planning
- Permit acquisition and regulatory approval processes
Equipment Procurement:
- Equipment ordering with appropriate lead time consideration
- Compatibility verification between different vendors and products
- Procurement of additional cables, connectors, and spare components
- Delivery timing coordination with installation schedule
Phase 2: Infrastructure Installation (Weeks 4-6)
Cabling Installation:
- Structured cabling installation to all planned locations
- Patch panel and network rack installation
- Comprehensive testing of all cable runs for continuity and performance
- Complete labeling for future maintenance requirements
Equipment Deployment:
- Core networking equipment installation and configuration
- Wireless access point installation and coverage optimization
- Basic security settings and access control configuration
- Connectivity and performance testing
Phase 3: Configuration and Optimization (Weeks 7-8)
Network Configuration:
- Wireless coverage optimization and performance tuning
- VLAN configuration and network segmentation implementation
- Monitoring and management system setup
- Backup and recovery procedure implementation
User Integration and Training:
- All user device connection and functionality testing
- Basic network operation training for staff
- Network settings and procedure documentation
- Regular maintenance and update schedule planning
Budget Planning and Cost Analysis
Current Market Pricing (2025)
Small Office (5-10 employees): $5,000-$12,000
- Business-grade router/firewall: $400-$1,000
- Managed switch with PoE: $500-$1,200
- 2-3 wireless access points: $600-$1,200
- Professional cabling installation: $2,000-$5,000
- Accessories (UPS, rack, cables): $500-$1,000
Medium Office (10-25 employees): $10,000-$25,000
- Professional gateway/UTM appliance: $1,000-$3,000
- Multiple switches and infrastructure: $2,000-$5,000
- 4-6 wireless access points: $1,200-$2,400
- Professional cabling installation: $4,000-$10,000
- Server room setup and accessories: $2,000-$5,000
Growing Business (25-50 employees): $25,000-$60,000
- Enterprise-grade security and routing: $3,000-$8,000
- High-performance switching infrastructure: $4,000-$12,000
- Comprehensive wireless coverage: $3,000-$8,000
- Professional installation and configuration: $10,000-$25,000
- Backup systems and redundancy: $4,000-$10,000
Additional Cost Considerations
- Building permits and inspection requirements
- Ongoing maintenance and support contracts
- Equipment lifecycle and replacement planning
- Staff training and certification programs
- Insurance and security compliance requirements
Common Implementation Challenges
Planning Considerations
Growth Underestimation:
Many businesses plan networks based solely on current requirements, necessitating expensive upgrades within 1-2 years. Planning for at least 50% growth in users and devices helps avoid this situation.
Security Planning:
Integrating security measures during initial design is typically more cost-effective and comprehensive than adding them after deployment. Consider planning for appropriate security controls from the project's beginning.
Equipment Selection:
While consumer equipment may appear cost-effective initially, business-grade equipment typically offers better reliability, security features, and scalability for growing organizations.
Implementation Considerations
Cable Management:
Proper cable management and labeling during installation simplifies future maintenance and troubleshooting. Investing time in organization during the initial setup typically reduces long-term operational costs.
Testing Procedures:
Comprehensive testing of every connection and documentation of performance baselines prevents performance issues and simplifies future troubleshooting procedures.
Documentation Requirements:
Complete documentation of network configuration makes future changes and troubleshooting more efficient and cost-effective.

Ongoing Management and Maintenance
Regular Maintenance Procedures
Monthly Tasks:
- Network performance and usage monitoring
- Security log and alert review
- Device firmware and software updates
- Backup and recovery procedure testing
Quarterly Tasks:
- Access control review and updates
- Capacity and performance trend assessment
- Future growth and change planning
- Staff training on new features or procedures
Annual Tasks:
- Comprehensive security audit
- Equipment lifecycle and replacement planning
- Budget planning for upgrades and improvements
- Disaster recovery testing and procedure updates
Performance Monitoring
Key Performance Indicators:
- Network utilization and bandwidth usage patterns
- Wireless coverage and performance metrics
- Security incidents and threat detection
- Equipment uptime and reliability statistics
- User satisfaction and support ticket trends
Monitoring Tools:
- Built-in device monitoring capabilities (UniFi Network application)
- Network monitoring software solutions (PRTG, SolarWinds)
- Security information and event management (SIEM) systems
- Help desk and ticketing system integration
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does small business network implementation typically take?
A typical 10-15-person office network requires 1-2 weeks from planning through completion, including equipment procurement, installation, and testing. Larger installations may require 2-4 weeks, depending on complexity.
What are the advantages of business-grade equipment over consumer options?
Business-grade equipment provides enhanced reliability, advanced security features, comprehensive management capabilities, and professional vendor support that consumer equipment cannot match for organizational environments.
Is professional installation necessary for network cabling?
Structured cabling in commercial environments typically requires professional installation to ensure building code compliance and optimal performance. However, qualified internal staff can sometimes manage equipment configuration.
What distinguishes Cat6 from Cat6A cable specifications?
Cat6A supports 10Gbps over longer distances (328 feet vs. 165 feet), providing enhanced shielding against interference. Cat6 is sufficient for most small business applications, while Cat6A offers improved future-proofing for high-bandwidth requirements.
How should South Florida businesses prepare for hurricane season?
Ensure equipment is properly mounted and secured, implement backup power solutions, establish cloud-based backup systems, and develop remote work capabilities so business operations can continue during power or connectivity interruptions.
What security features should small business networks include?
Essential security features include enterprise firewall protection with AI threat detection, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) for remote workers, wireless security (WPA3), network segmentation, regular security updates, and comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities. Traditional VPNs are being replaced by identity-based access controls that limit lateral movement risks.
What budget should I allocate for small business network infrastructure?
Budget $400-$1,200 per employee for complete network infrastructure, including equipment, installation, and initial configuration. Costs vary significantly based on specific requirements and facility complexity.
Can network infrastructure be expanded without major modifications?
With appropriate initial planning, networks can typically be expanded through additional switches, access points, and cabling. Planning for growth during the initial design phase is essential for cost-effective expansion.
What factors most significantly impact network reliability?
The quality of initial installation and ongoing maintenance procedures is the primary factor affecting network reliability. Even high-quality equipment will underperform if not correctly installed, configured, and maintained.
Should network management be handled internally or outsourced?
Organizations with dedicated IT staff can often manage routine network maintenance, while most small businesses benefit from professional support for complex troubleshooting, security monitoring, and strategic technology planning.
Implementation Support: Our Miami-based team designs and implements scalable network solutions for growing businesses. Contact us for a comprehensive consultation and assessment tailored to your specific business requirements.
Related Resources:
Related Articles
More from Network Infrastructure

Multi-Gig Network Upgrade Guide for Small Business: 2.5G, 5G & 10G in 2026
Complete guide to upgrading your small business network to multi-gigabit speeds. Learn whether 2.5G, 5G, or 10GbE is right for you, what it costs, and how to implement it over existing infrastructure.
35 min read

Complete Network Visibility: The Business Case for Managed Infrastructure
Understanding the operational advantages of managed network infrastructure vs unmanaged equipment. Covers cost-benefit analysis, UniFi switches, implementation strategies, and ROI timeline.
11 min read

Professional WiFi 7 Network Implementation: Complete Business Guide
Complete guide to professional WiFi 7 network implementation for businesses. Covers infrastructure planning, UniFi equipment selection, cost analysis, and implementation best practices.
20 min read