A technical analysis of Ubiquiti's UniFi ecosystem for business networking and security
Business networking decisions involve balancing performance, security, and budget considerations. Enterprise solutions often exceed small business requirements and budgets, while consumer equipment typically lacks the features and reliability needed for professional environments. UniFi positions itself as a middle-ground solution for businesses seeking enterprise-grade capabilities without enterprise-level complexity.
As IT consultants who've deployed UniFi systems across South Florida in 2025, we've gained practical experience with installations ranging from warehouse facilities to professional offices and even a remote farm operation near the Everglades. This comprehensive review examines real-world performance, total cost considerations, and whether UniFi's unified management approach effectively addresses business networking requirements.
Key Takeaways
| Category | Rating | Key Points |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 12.5 Gbps routing with full security enabled (EFG) |
| Management | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | Unified interface, but requires networking knowledge. |
| Security | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | 95,000+ threat signatures with Proofpoint integration |
| Value | ⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ | Competitive vs enterprise, but ecosystem lock-in. |
| Best For | SMBs | 5-500 employees needing professional networking |
What is UniFi IT Solutions?
UniFi is a comprehensive IT management platform that combines powerful internet gateways with scalable WiFi and switching, providing real-time traffic dashboards, visual topology maps, and optimization tips. Unlike traditional networking solutions that require separate management systems for different components, UniFi consolidates network infrastructure, security, and surveillance into a unified ecosystem.
The platform operates on a unique philosophy: license-free networking for core functionality combined with optional subscription-based services for advanced threat intelligence. This approach allows businesses to deploy professional-grade networking without the ongoing licensing costs typically associated with enterprise solutions.
Core Platform Components
- Network Infrastructure: Next-generation Cloud Gateways, managed PoE switches, and WiFi 7 access points with 6 GHz support
- Security Features: Comprehensive IDS/IPS, advanced firewall, VPN server, and Proofpoint threat intelligence
- Surveillance & Access: UniFi Protect 5 with video management, AI-powered analytics, and door access control
- Management Software: UniFi Network 9 with zone-based firewall controls and SD-WAN capabilities
Gateway Hardware Comparison (2025)
| Model | Throughput | Max Devices | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Fortress Gateway | 12.5 Gbps | 500+ UniFi devices | 25G ports, redundant PSU, HA | $1,999+ |
| Dream Machine Pro Max | 5 Gbps | 1000s of clients | RAID storage, HA support | $599+ |
| Dream Machine Pro SE | 3.5 Gbps | 100s of clients | Built-in PoE switching | $499+ |
| Dream Machine Pro | 3.5 Gbps | 100s of clients | 8-port switch, proven reliability | $379+ |
Enterprise Fortress Gateway – The Flagship
The Enterprise Fortress Gateway represents UniFi's flagship security appliance, designed for demanding enterprise environments. With 12.5 Gbps IPS routing capability while maintaining full security features, it addresses the performance limitations that have historically plagued security-enabled network equipment.
Key Enterprise Features:
- Support for 500+ UniFi devices and 5,000+ simultaneous clients
- Multiple high-speed ports: (2) 25G SFP28, (2) 10G SFP+, (2) 2.5 GbE RJ45
- Shadow Mode High Availability with automatic failover
- License-free SSL/TLS inspection with NeXT AI capabilities
- Redundant hot-swappable power supplies
- 90-day professional support included
Dream Machine Pro Max – The Sweet Spot
The Dream Machine Pro Max bridges the gap between small business and enterprise requirements, offering enhanced computing performance that supports thousands of client devices while maintaining 5 Gbps routing with full DPI and IPS security enabled.
Understanding Power over Ethernet (PoE) requirements becomes essential when deploying UniFi access points, as proper power planning ensures optimal performance across your network infrastructure.
WiFi 7 Access Point Lineup
| Model | Streams | Max Throughput | Coverage | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U7 Pro Max | 8 spatial streams | 15 Gbps | 160 m² (1,750 ft²) | $280 |
| U7 Pro | 6 spatial streams | 9.3 Gbps | 140 m² (1,500 ft²) | $200 |
| U7 Lite | 4 spatial streams | 5.8 Gbps | 115 m² (1250 ft²) | $100 |
| U7 Pro Wall | 6 spatial streams | 9.3 Gbps | 140 m² (1,500 ft²) | $200 |
For businesses experiencing WiFi performance issues, upgrading to WiFi 7 technology can provide significant improvements in both speed and device capacity, particularly in high-density environments with numerous concurrent users.
Security Features Deep Dive
Built-in Protection Capabilities
UniFi gateways include comprehensive security features that work together to create multiple layers of protection:
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): Wire-speed analysis without performance degradation
- Application-Aware Filtering: Beyond port-based rules to identify specific applications
- Geographic IP Blocking: Restrict access from high-risk countries or regions
- Custom Rule Creation: Tailor security policies to specific business requirements
- VPN Server Capabilities: Secure remote access for distributed teams
- Behavioral Anomaly Detection: Identify unusual network patterns
CyberSecure by Proofpoint Integration
Since its introduction in 2024, UniFi's CyberSecure by Proofpoint has become a mature and proven enhancement to the platform's security capabilities. The service operates entirely on local gateway hardware, preserving data privacy while reducing latency compared to cloud-based security solutions.
| Feature | Standard ($99/year) | Enterprise ($499/year) |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Signatures | 55,000+ across 53 categories | 95,000+ with additional categories |
| Update Frequency | 30-50+ additions weekly | Real-time + priority updates |
| Gateway Support | All except UXG Lite | Enterprise Fortress, UXG Enterprise |
| Advanced Analytics | Basic reporting | Enhanced reporting & analytics |
| Professional Support | Community support | Professional support integration |
UniFi Network 9.0: Major Software Evolution
Released in January 2025, UniFi Network 9.0 represents a significant evolution in network management capabilities. It introduces several enterprise-grade features that enhance security and scalability.
Zone-Based Firewall Management
The new zone-based approach simplifies network traffic management by grouping devices and services into logical zones (Internal, External, Gateway, VPN). This approach replaces the complexity of managing countless individual VLAN or device rules with a streamlined policy framework.
Benefits of Zone-Based Management:
- Reduced administrative overhead in complex networks
- More intuitive security policy creation
- Better scalability across large deployments
- Simplified troubleshooting and audit processes
Enhanced SD-WAN Capabilities
SiteMagic SD-WAN provides license-free connectivity for up to 1,000 locations through two topology options:
- Mesh Topology (up to 20 sites): Straightforward connectivity for smaller multi-location businesses
- Hub-and-Spoke (up to 1,000 sites): Massive deployments with multiple tunnels and secondary failover hubs
Local Network API
The Local Network API enables direct access to UniFi deployments without routing traffic through cloud services, providing:
- Real-time monitoring of CPU, memory, and uptime data
- Live statistics for WiFi, wired, and VPN clients
- Local data control without cloud dependencies
- Enhanced privacy for sensitive environments
Real-World Performance Analysis
Our 2025 Deployment Experience
Having completed dozens of installations across South Florida this year, we can provide practical insights into UniFi's capabilities across different environments:
✅ Warehouse Deployments
Large-scale warehouse facilities benefit from UniFi's centralized management and scalable wireless coverage. The platform handles industrial environments well, with access points maintaining connectivity across extensive floor areas despite challenges from:
- Metal shelving is causing RF interference
- High ceilings require careful coverage planning
- Industrial equipment generating electromagnetic noise
- Extreme temperature variations
✅ Professional Offices
Office environments showcase UniFi's strengths in VLAN capabilities for network segmentation, guest access isolation, and device management. The unified controller simplifies management of multiple access points and user policies across different departments.
For comprehensive guidance on professional network deployments, our future-proof office network guide provides detailed implementation strategies based on real-world deployment experience.
✅ Remote Locations
Our most challenging installation involved a remote farm operation near the Everglades, where UniFi's remote management capabilities proved invaluable. Despite isolated location challenges, including:
- Limited internet connectivity
- Extreme weather conditions
- No local technical support
- Power reliability concerns
The platform's VPN functionality and remote monitoring enabled reliable connectivity and ongoing management.
Performance Metrics
Current-generation gateways demonstrate substantial improvements over earlier models:
| Gateway Model | Throughput (Security On) | Previous Generation | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enterprise Fortress Gateway | 12.5 Gbps | N/A (New) | New flagship |
| Dream Machine Pro Max | 5 Gbps | 3.5 Gbps | +43% |
| Dream Machine Pro | 3.5 Gbps | 1.8 Gbps | +94% |
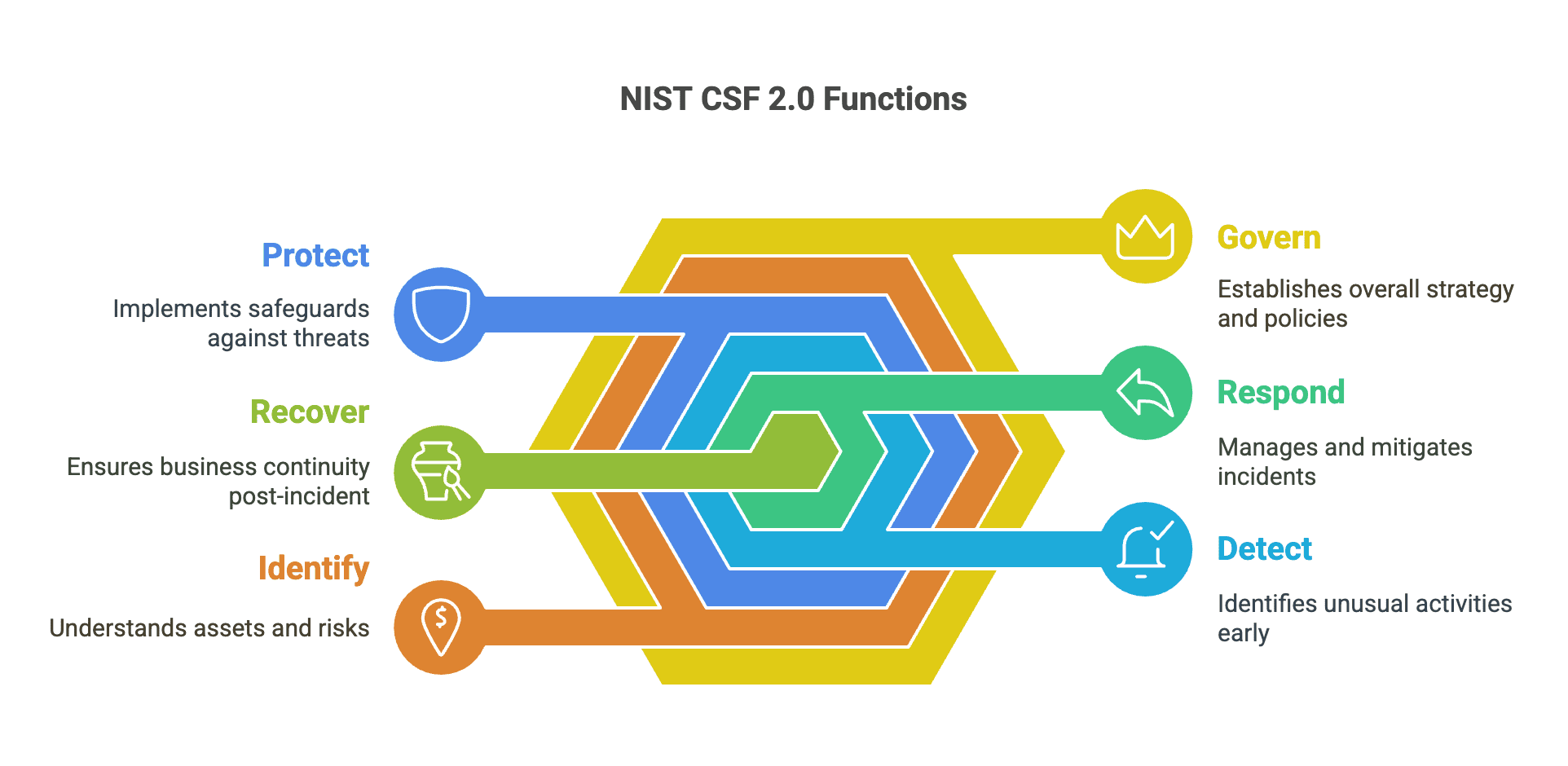
NIST Cybersecurity Framework Alignment
UniFi's security architecture aligns well with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework, providing organizations with a structured approach to cybersecurity implementation:
The Six Core Functions
| NIST Function | UniFi Capabilities |
|---|---|
| GOVERN | Centralized policy enforcement, risk-based configurations, and asset management |
| IDENTIFY | Network topology visualization, asset discovery, and traffic analysis |
| PROTECT | VLAN segmentation, encrypted tunnels, and access control |
| DETECT | 95,000+ threat signatures, anomaly detection, centralized logging |
| RESPOND | Automated threat blocking, integrated notifications, and forensic analysis |
| RECOVER | RAID storage options, configuration management, and communication coordination |
Comprehensive Pros and Cons
✅ Major Advantages
Unified Management Excellence
- Single-click adoption of network appliances with automatic firmware installation
- Comprehensive network coverage through integrated hardware solutions
- Augmented reality features in mobile apps show live port overlays
- Visual topology maps for intuitive network understanding
Security Integration
- Local threat processing preserves data privacy
- Professional-grade security at accessible price points
- Regular security updates through established threat intelligence partnerships
- No cloud dependencies for core security functions
Scalability and Performance
- Enterprise-grade performance with simplified management
- Future-proof hardware supporting emerging technologies
- Modular expansion without compatibility concerns
- License-free core functionality with optional premium services
❌ Notable Limitations
Learning Curve Considerations
- Extensive feature sets can overwhelm networking newcomers
- Advanced VLAN creation requires an understanding of network protocols
- Complex configurations may require professional assistance
- UniFi-specific expertise is needed for optimal deployment
Ecosystem Dependencies
- Vendor lock-in scenarios with limited third-party compatibility
- Infrastructure replacement may be required for migration
- Higher initial costs compared to basic networking solutions
- Reduced flexibility compared to open-architecture solutions
Implementation Complexity Levels
| Complexity | Use Cases | Requirements | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Small office (5-25 users) Basic WiFi & internet |
Minimal configuration Standard firewall protection |
1-2 days |
| Medium | Multi-site connectivity VLAN segmentation Video surveillance |
Network planning VLAN design Guest isolation |
3-5 days |
| High | Advanced VLANs Custom routing Compliance requirements |
Networking expertise Professional assistance Compliance knowledge |
1-2 weeks |
Pricing and Value Analysis (2025)
Complete Investment Breakdown
| Deployment Tier | Initial Investment | Typical Components | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level | $600-2,000 | Dream Machine + U7 Lite APs + basic switches | Small offices (5-15 users) |
| Professional | $2,500-8,000 | Dream Machine Pro Max + U7 Pro APs + PoE switches | Medium businesses (15-50 users) |
| Enterprise | $8,000+ | Enterprise Fortress Gateway + U7 Pro Max + HA setup | Large businesses (50+ users) |
Ongoing Costs
- CyberSecure Standard: $99/year per site (55,000+ signatures)
- CyberSecure Enterprise: $499/year per site (95,000+ signatures)
- Professional Support: Included with EFG, available separately for other models
- Core Functionality: License-free with firmware updates at no cost
Competitive Analysis
| Platform | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| UniFi | Unified management, competitive pricing, and local processing | Learning curve, ecosystem lock-in | SMBs seeking balance |
| Cisco Meraki | Extensive features, established support | High ongoing costs, cloud dependency | Large enterprises |
| SonicWall | Deep security customization | Separate management systems, complexity | Security-focused orgs |
| Fortinet FortiGate | Comprehensive security fabric | Complex configuration, high TCO | Enterprise security |
When to Choose UniFi
✅ Ideal Candidates
- Small to medium businesses requiring professional network capabilities without enterprise complexity
- Privacy-conscious organizations prioritize local data processing over cloud solutions
- Growing companies need scalable solutions that evolve with business needs
- Technology-forward environments implementing IoT devices and modern wireless standards
- Multi-location businesses are benefiting from centralized management and SD-WAN capabilities
❌ Consider Alternatives If
- Maximum flexibility is required with extensive third-party integration needs
- Limited technical expertise is available for deployment and ongoing management
- Existing infrastructure represents a significant investment that cannot be replaced
- Compliance requirements mandate specific vendor certifications not available with UniFi
Final Verdict
Based on our extensive 2025 deployment experience across diverse South Florida environments, UniFi has matured into a compelling networking platform that successfully balances professional capabilities with manageable complexity. The hardware performance improvements, particularly in the Enterprise Fortress Gateway, address previous concerns about security feature overhead.
Key Takeaways from Our Experience:
- Performance delivery: The 12.5 Gbps Enterprise Fortress Gateway and 5 Gbps Dream Machine Pro Max provide real-world performance that matches specifications
- Versatility proven: Successful deployments from air-conditioned offices to industrial warehouses to remote agricultural facilities.
- Management efficiency: Unified interface significantly reduces operational complexity versus multi-vendor solutions
- Security maturity: CyberSecure by Proofpoint integration provides enterprise-grade threat intelligence with local processing
The CyberSecure by Proofpoint integration provides enterprise-grade threat intelligence while maintaining local processing. With over 95,000 signatures in the enterprise tier and weekly updates, security capabilities now match many traditional enterprise solutions, supporting comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks as outlined by NIST CSF 2.0.
However, organizations should carefully evaluate the ecosystem approach, which represents both UniFi's primary strength and limitation. The learning curve for advanced features and the requirement for UniFi-specific expertise should factor into implementation planning.
UniFi's 2025 offerings represent a practical choice in the current networking landscape for businesses prioritizing security, performance, and operational simplicity. When planning multi-gigabit network upgrades, UniFi provides a clear path from small business needs to enterprise-scale deployments without requiring platform changes.
This review reflects the current state of UniFi IT Solutions as of June 2025. The rapidly evolving nature of networking technology means prospective users should verify current specifications, pricing, and feature availability before making implementation decisions.
Disclosure: iFeelTech participates in the Ubiquiti Creator Program.
We may earn a commission when you purchase UniFi products through our links at no
additional cost to you. Our recommendations are based on professional experience and testing.