A 10-Step Secrets Hygiene Checklist for SMB Development & Operations Teams
With data breaches now costing U.S. businesses $10.22 million on average and secrets sprawl accelerating 25% annually, this comprehensive 10-step checklist helps SMB dev/ops teams implement robust credential security and protect against AI-driven threats.

Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Key Takeaway
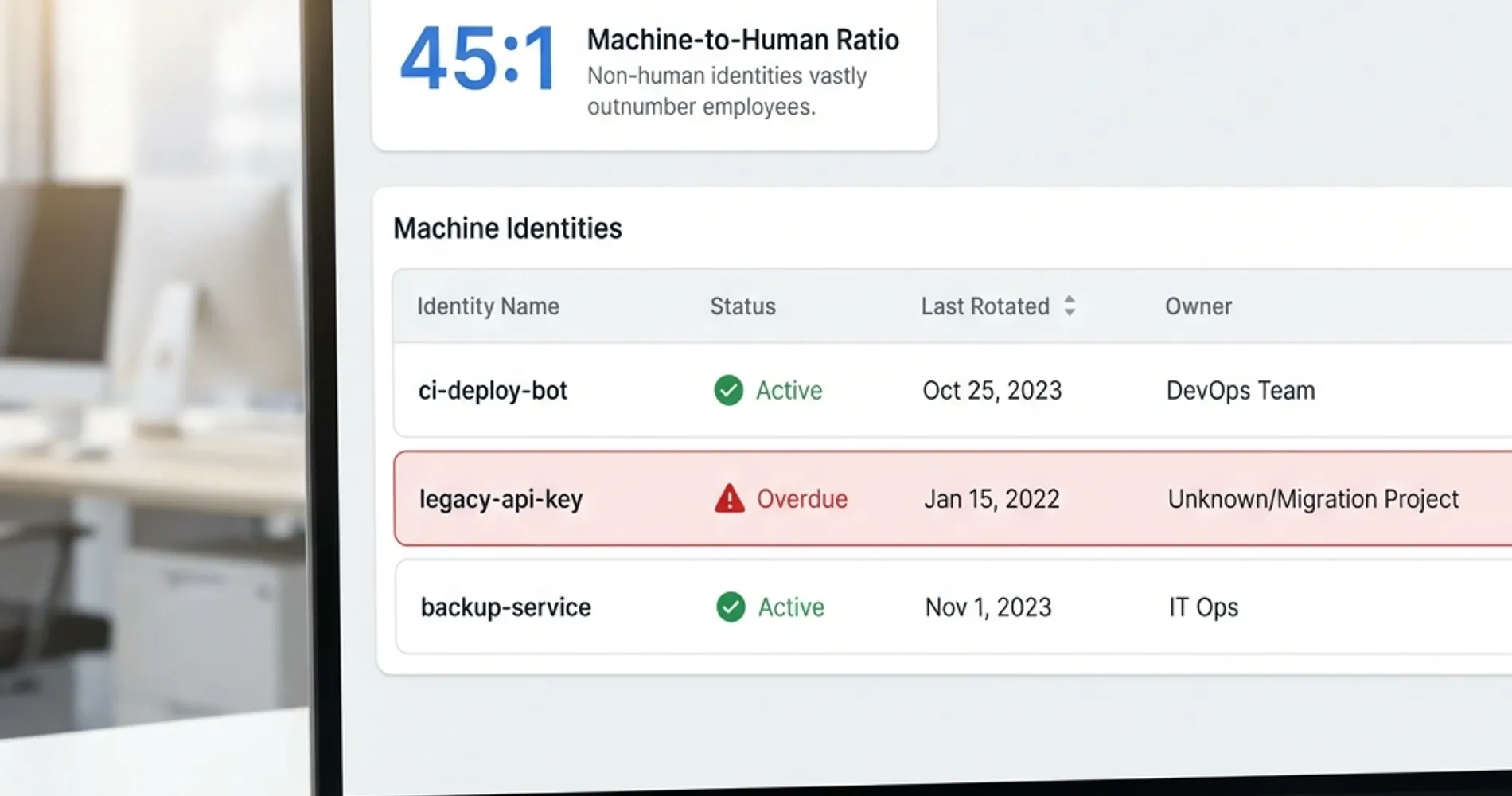
Data breaches now cost U.S. businesses an average of $10.22 million, with secrets sprawl accelerating by 25% annually. With 65% of leading AI companies having leaked verified secrets and machine identities outnumbering humans 45:1, this comprehensive checklist provides 10 systematic actions development and operations teams can implement to establish robust credential security and prevent exposure before it leads to costly compromise.
Understanding the Credential Security Challenge
Security teams are drowning in machine credentials while breach costs reach record highs. U.S. businesses now face an average breach cost of $10.22 million—while the global average dropped to $4.44 million in 2025, highlighting how U.S. regulatory and legal environments amplify financial exposure. For SMBs, a single credential-based breach represents a critical operational risk that can threaten business continuity and customer trust.
Secrets sprawl is accelerating by 25% annually. GitGuardian's 2025 State of Secrets Sprawl Report documented 23.8 million secrets on public GitHub alone. More critically, 90% of exposed valid secrets remain active five days after notification, creating extended windows for attackers to exploit credentials discovered through automated scanning.
The threat landscape has evolved beyond traditional code repositories. Recent research reveals that 65% of leading AI companies have accidentally leaked verified secrets on GitHub, introducing new attack vectors through "Shadow AI"—where developers inadvertently expose credentials by pasting code into unsanctioned LLMs or through prompt injection vulnerabilities. Additionally, machine identities (API keys, service accounts) now outnumber human identities over 40:1, creating massive blind spots in credential management that attackers increasingly exploit for lateral movement.
The 10-Step Secrets Hygiene Checklist
This checklist prioritizes immediate impact and practical implementation for development and operations teams managing infrastructure at scale. Each step includes specific tools, implementation guidance, and expected outcomes based on industry analysis and proven deployment patterns.
Step 1: Deploy Repository Scanners Immediately
Priority: Critical | Implementation Time: 2-4 hours | ROI: Immediate
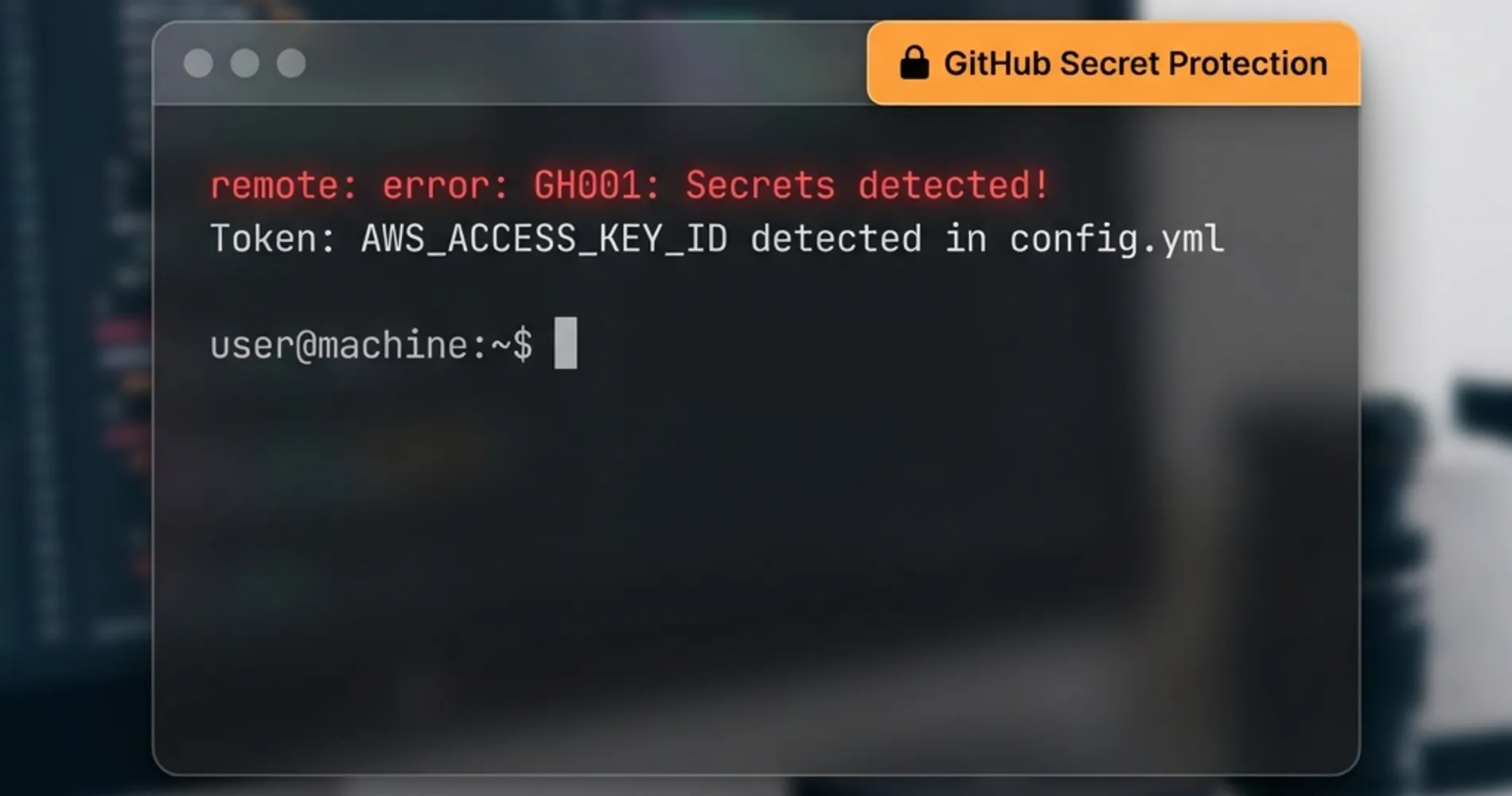
Repository scanning provides the first line of defense against credential exposure, intercepting secrets before they propagate beyond code management systems. GitHub's secret scanning technology encompasses over 200 token types and patterns from more than 180 service providers, offering industry-leading detection capabilities for public repositories.
Implementation Options
- GitHub Secret Protection: Push protection now available as a standalone add-on at $19 per active committer/month (unbundled from Advanced Security since mid-2025)
- GitGuardian: Enterprise-grade scanning with multi-repository visibility and automated remediation workflows
- TruffleHog: Open-source scanning with container and CI/CD integration capabilities
Immediate Actions
- Enable GitHub's push protection for all repositories (available by default for public repos)
- Configure organization-wide scanning policies with appropriate alert routing
- Establish alert routing to both security and development teams
- Create remediation playbooks for different secret types and risk levels
Expected Outcome: Prevent 60-80% of secrets from entering repository history, significantly reducing downstream remediation effort and exposure windows.
Step 2: Implement Pre-Commit Hooks
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 1-2 hours per repository | ROI: High
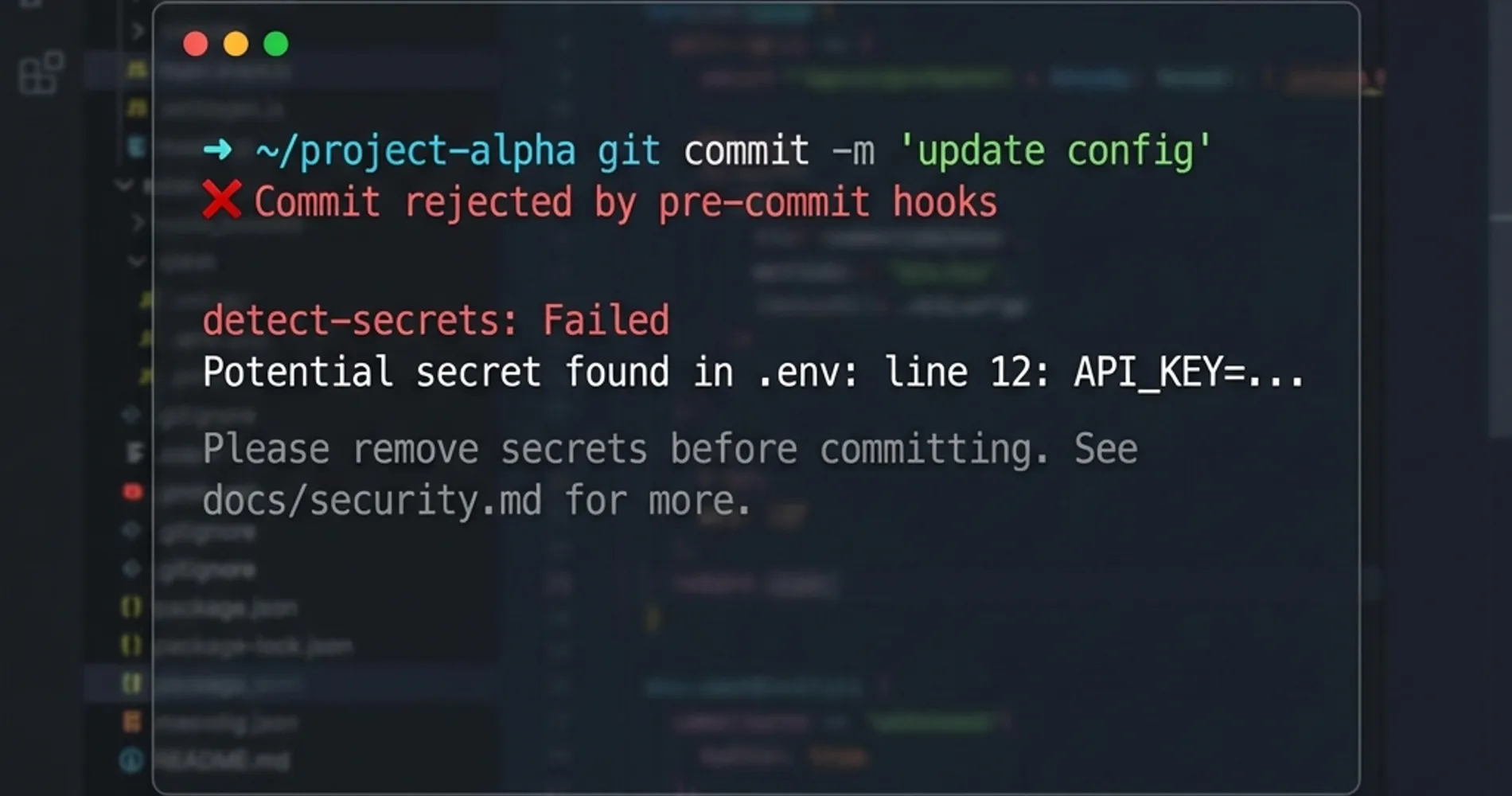
Pre-commit hooks provide the earliest possible intervention point in the development workflow, catching secrets before they enter version control. While these can be bypassed locally, they serve as essential education and early warning systems for development teams.
Recommended Tools
- GitGuardian Shield (ggshield): Leverages GitGuardian's detection engine through a command-line interface
- detect-secrets: Yelp's enterprise-friendly approach with baseline management capabilities
- git-secrets: AWS-developed tool with strong pattern matching for cloud credentials
Implementation with pre-commit framework:
# .pre-commit-config.yaml
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/gitguardian/ggshield
rev: v1.25.0
hooks:
- id: ggshield
language: python
stages: [commit]
Configuration Best Practices
- Create baseline files for existing repositories to handle legacy secrets appropriately
- Configure custom patterns for proprietary token formats and internal systems
- Establish bypass procedures for emergency commits with proper approval workflows
- Include comprehensive training documentation for developers on installation and maintenance
Expected Outcome: Reduce accidental secret commits by 70-90% while building security awareness and best practices across development teams.
Pro-Tip: Preventing AI-Driven Secrets Leaks
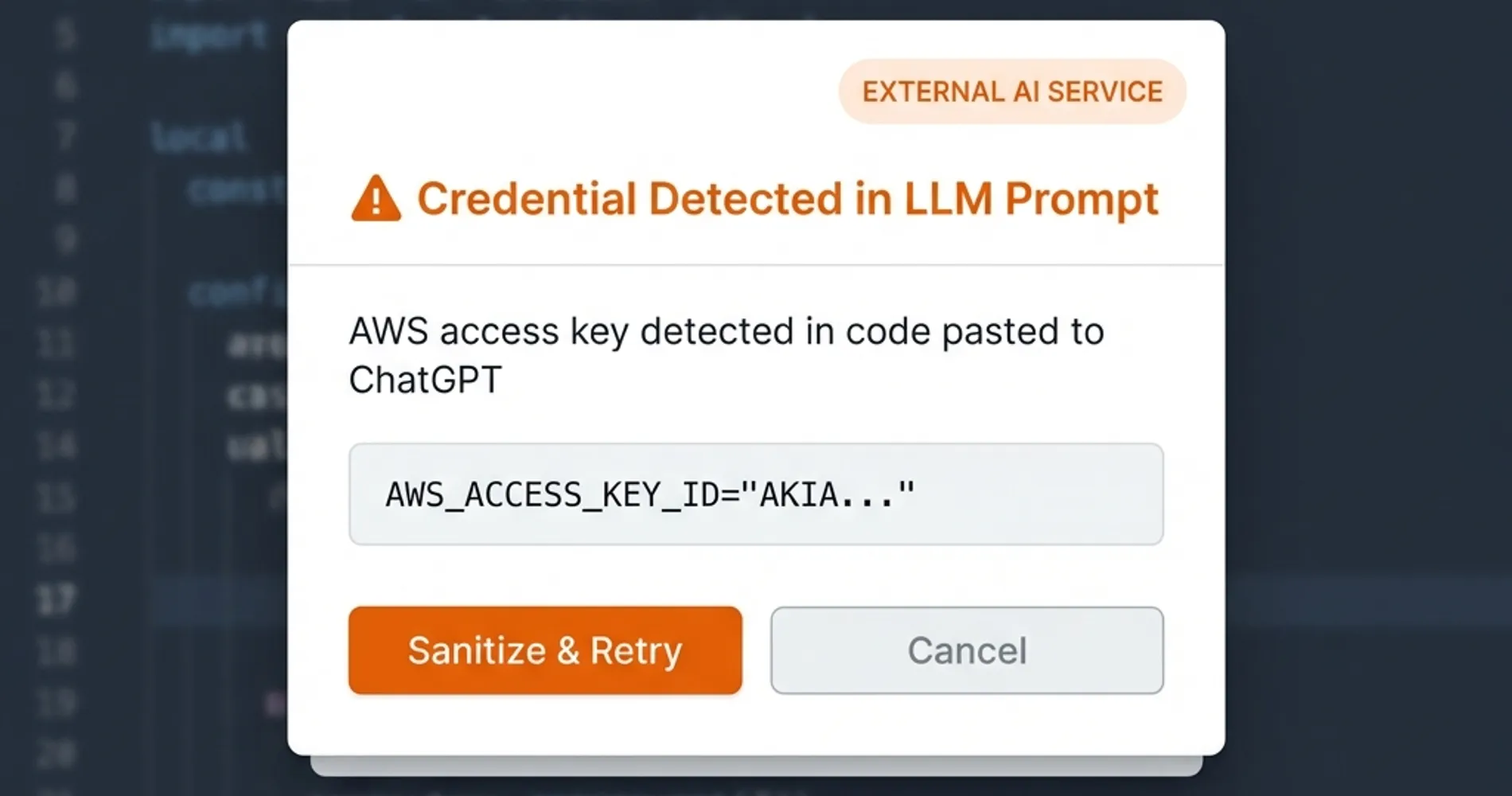
The Shadow AI Threat: With 65% of leading AI companies having leaked verified secrets, developers must adopt new security practices for AI interactions:
- Never paste code containing credentials into LLMs (ChatGPT, Claude, Copilot Chat, etc.) without sanitizing first
- Implement AI usage policies that explicitly prohibit sharing production code or configuration files
- Use AI-safe code snippets by replacing all real credentials with placeholder values before sharing
- Monitor for prompt injection attacks where malicious actors attempt to extract credentials through crafted prompts
- Deploy AI gateway solutions that scan and redact sensitive information before it reaches external LLM services
This is the fastest-growing credential exposure vector in 2026. Organizations should treat AI tools as untrusted third parties and implement "Developer-in-the-loop" workflows that automatically flag and sanitize code before AI submission.
Step 3: Enforce Short Token Lifetimes
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 2-8 hours | ROI: Very High
Shorter token lifetimes dramatically reduce the potential impact when credentials are compromised. With machine identities (Non-Human Identities/NHIs) outnumbering humans over 40:1, these service accounts, API keys, and automated credentials represent the primary target for lateral movement attacks. Research shows that 70% of secrets leaked in 2022 remained active years later, highlighting the critical remediation gap. Modern secrets management platforms like HashiCorp Vault can generate secrets on demand for systems, including AWS and SQL databases, enabling just-in-time access patterns that minimize exposure windows and address the NHI blind spot.
Implementation Strategy
- Cloud Services: Configure 1-4 hour lifetimes for development environments, 24-hour maximum for production systems
- Database Credentials: Implement daily rotation for application service accounts with automated renewal
- API Keys: Set 7-30 day maximum lifetimes with automated renewal processes and health monitoring
- Service-to-Service Authentication: Transition to certificate-based authentication with 90-day maximum validity periods
Automation Requirements
- Integrate rotation schedules with CI/CD pipelines to prevent service disruption
- Implement comprehensive health checks to verify credential functionality post-rotation
- Create robust fallback mechanisms for rotation failures and edge cases
- Monitor application logs systematically for authentication errors during transition periods
- Deploy Developer-in-the-loop workflows that automatically nudge developers to rotate keys immediately upon exposure detection
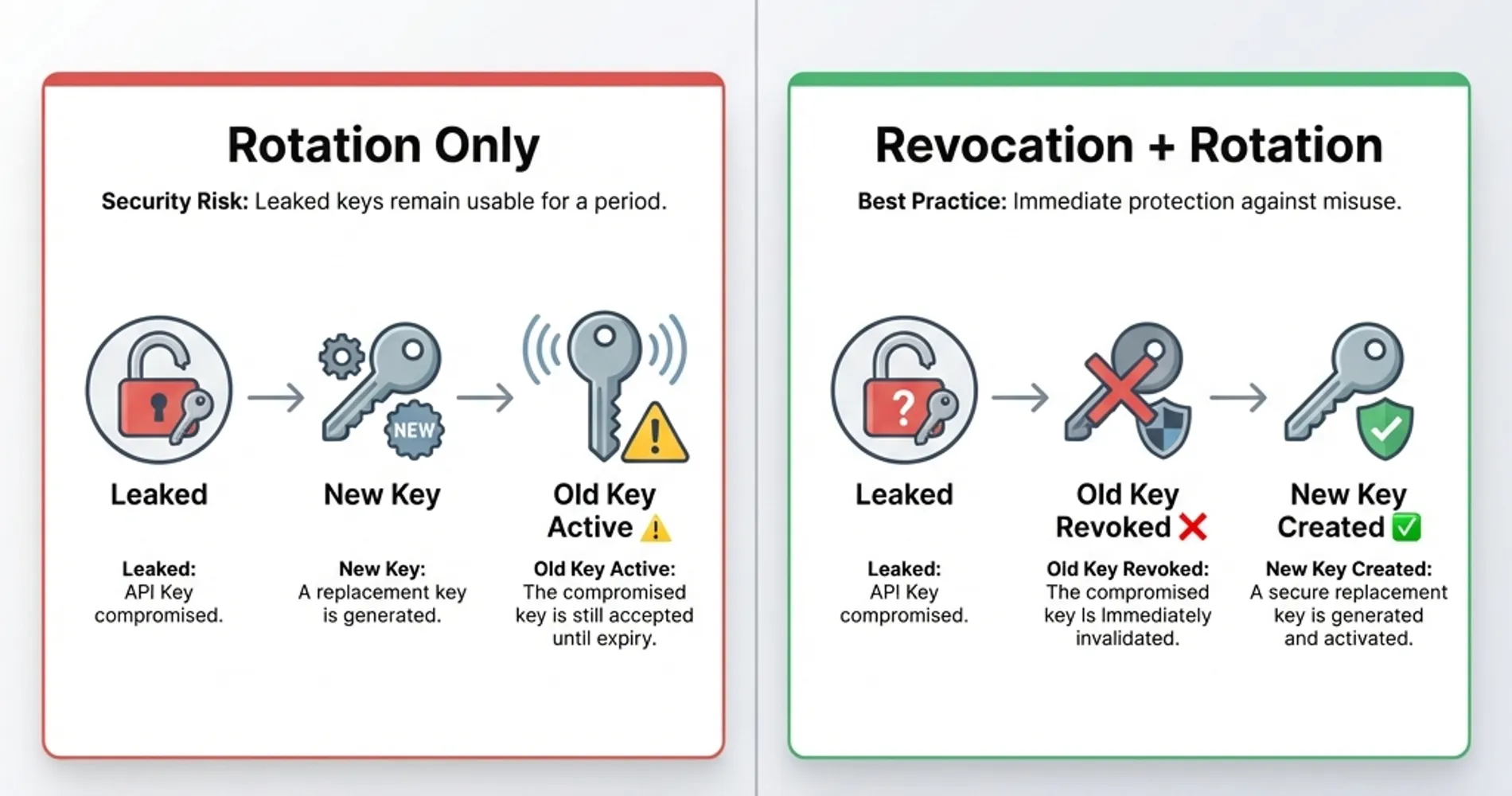
- Implement immediate revocation capabilities: When secrets are exposed, revoke the compromised credential at the provider level before rotating—rotation alone leaves the old key active
Critical: Revocation vs. Rotation
Rotation creates a new credential for future use, but revocation kills the old credential immediately. When a secret is discovered publicly (Step 1), you must revoke the compromised key at the provider level (AWS IAM, GitHub tokens, API provider dashboards) to ensure the exposed credential cannot be used, even if an attacker already copied it. Only then should you rotate to a new credential.
Expected Outcome: Reduce average credential exposure time from months or weeks to hours, significantly limiting attacker dwell time and lateral movement capabilities. Automated remediation workflows address the critical gap where 70% of leaked secrets remain active indefinitely.
Step 4: Deploy SSO/IdP for All SaaS Tools
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 1-3 days | ROI: Very High
Single sign-on eliminates password reuse while providing centralized access control across the entire SaaS ecosystem. ConnectWise's 2025 SMB cybersecurity research indicates that 58% of small and medium businesses now view improved security as a key benefit of working with managed service providers. SSO implementation represents a primary security enhancement driving this perception.
Enterprise-Grade Solutions
- Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD): Essential for enforcing conditional access policies and integrating with Microsoft 365 environments
- Okta: Provides centralized SSO management with 7,000+ pre-built integrations for rapid deployment
- Google Workspace Identity: Optimal for Google-centric environments with native Workspace security controls
Implementation Priorities
- Critical Infrastructure: Code repositories, cloud management consoles, monitoring and alerting tools
- Collaboration Platforms: Slack, Microsoft Teams, project management and communication tools
- Development Tools: Container registries, CI/CD platforms, testing and deployment environments
- Business Applications: CRM systems, ERP platforms, financial and administrative tools
Configuration Best Practices
- Require phishing-resistant MFA (FIDO2/Passkeys) for all administrative access and privileged accounts—standard MFA (SMS/Push) is easily bypassed by modern Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) attacks
- Implement conditional access policies based on device trust status and geographic location
- Configure session timeouts appropriate to risk levels and business requirements
- Establish comprehensive break-glass access procedures for emergency scenarios
Expected Outcome: Eliminate 90%+ of password-based authentication while gaining centralized visibility and control over access patterns. For comprehensive password security beyond SSO, consider implementing enterprise password managers for remaining legacy systems and personal credentials.
Step 5: Use Honeytokens for Detection
Priority: Medium | Implementation Time: 2-4 hours | ROI: High
Honeytokens provide early warning systems that detect unauthorized access attempts or credential theft activities. These intentionally fake credentials trigger alerts when accessed, providing valuable visibility into potential compromise scenarios and attacker behavior patterns.
Implementation Strategies
- Repository Honeytokens: Place convincing fake API keys in documentation, configuration templates, and inactive code paths
- Environment Honeytokens: Deploy fake database credentials and service account tokens in staging environments
- Documentation Honeytokens: Embed fake credentials in internal wikis, runbooks, and technical documentation
- Infrastructure Honeytokens: Create fake cloud service credentials with logging-only permissions for monitoring access attempts
Deployment Best Practices
- Use realistic but deliberately fake patterns that won't interfere with legitimate operations
- Configure immediate alerting with detailed contextual information about access attempts
- Integrate honeytoken alerts with SIEM platforms and incident response workflows
- Establish regular rotation schedules for honeytokens to maintain detection effectiveness
Expected Outcome: Gain early warning capabilities for credential theft activities and improve incident response time by 50-75% through proactive threat detection.
Step 6: Scan Container Images for Secrets
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 2-6 hours | ROI: High
Container images frequently contain embedded secrets that persist across deployments and environments. GitGuardian's comprehensive analysis of 15 million public Docker images discovered over 100,000 valid secrets, including AWS keys and GitHub tokens from major organizations. These secrets often survive multiple image builds and deployments, creating persistent security vulnerabilities throughout the software supply chain.
Scanning Integration Points
- Build Pipeline: Scan images before pushing to registries with automated failure conditions
- Registry Scanning: Continuous scanning of stored images with regular updates
- Runtime Scanning: Detect secrets in running containers and active deployments
- Compliance Scanning: Regular audits of production image repositories for ongoing validation
Recommended Tools
- Trivy: Open-source scanner with comprehensive secret detection capabilities and extensive format support
- Twistlock/Prisma Cloud: Enterprise container security platform with integrated secrets scanning
- GitGuardian: Container image scanning with AI-enhanced secret-specific detection capabilities
CI/CD integration example:
container_scan:
stage: security
script:
- trivy image --exit-code 1 --format template --template "@contrib/sarif.tpl" $IMAGE_NAME
- ggshield container-scan $IMAGE_NAME
Expected Outcome: Eliminate 95%+ of secrets in container images while establishing secure container build practices and deployment procedures.
Step 7: Monitor Collaboration Platforms
Priority: Medium | Implementation Time: 3-8 hours | ROI: Medium
Collaboration platforms, including Slack, Microsoft Teams, and project management tools, frequently contain inadvertently shared credentials. GitGuardian's 2025 analysis indicates that incidents in collaboration tools are classified as highly critical or urgent at a higher proportion than in code repositories. Yet, these platforms often lack built-in security safeguards for credential detection and protection.
Monitoring Strategies
- Chat Platform Scanning: Deploy automated bots that scan for credential patterns in real-time message streams
- File Share Monitoring: Scan uploaded documents and files for embedded secrets and sensitive information
- Integration Monitoring: Audit third-party integrations systematically for credential exposure risks
- Historical Scanning: Regular analysis of existing message and file histories with appropriate retention policies
Platform-Specific Approaches
- Slack: Utilize GitGuardian's Slack integration for real-time secret detection with contextual remediation guidance
- Microsoft Teams: Implement Microsoft Purview for comprehensive data loss prevention and compliance monitoring
- Confluence/Jira: Configure scanning workflows for documentation and ticket systems with automated alerting
- Google Workspace: Enable advanced security features with comprehensive Drive file scanning capabilities
Expected Outcome: Reduce credential exposure in collaboration platforms by 80-90% while maintaining the effectiveness of team productivity and communication flow.
Step 8: Implement Secrets Rotation Automation
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 1-2 weeks | ROI: Very High
Automated rotation eliminates human error in credential management while ensuring consistent security practices across all systems and environments. This systematic approach reduces operational overhead while improving security posture through regular credential refresh cycles.
Rotation Framework Design
- Discovery & NHI Inventory: Automated inventory and cataloging of all credentials across systems and environments—with machine identities outnumbering humans 40:1, maintaining a comprehensive Non-Human Identity (NHI) inventory is critical for visibility
- Classification: Risk-based categorization determining appropriate rotation frequencies and priorities
- Orchestration: Coordinated rotation across dependent systems with proper sequencing and rollback capabilities
- Verification: Comprehensive health checks confirming successful rotation completion and system functionality
Non-Human Identity (NHI) Governance
With machine identities outnumbering humans over 40:1, organizations must implement dedicated NHI governance:
- Inventory all service accounts, API keys, and machine credentials across cloud providers, CI/CD systems, and applications
- Establish ownership and accountability for each NHI—assign a human owner responsible for lifecycle management
- Implement least-privilege access for all machine identities with regular access reviews
- Monitor NHI usage patterns to detect anomalous behavior indicating compromise or misuse
- Automate NHI lifecycle management including creation, rotation, and decommissioning
These "invisible" credentials are the primary target for lateral movement attacks and represent the largest blind spot in most security programs.
Technology Integration
- HashiCorp Vault: Dynamic secrets generation with automated lifecycle management and extensive integration support
- AWS Secrets Manager: Native rotation for AWS services with Lambda integration and automated scheduling
- Azure Key Vault: Integrated rotation for Azure resources and applications with managed identity support
- CyberArk: Enterprise privileged access management solution with comprehensive rotation capabilities
Implementation Phases
- Phase 1: Database credentials and service accounts with clear dependencies
- Phase 2: Cloud service credentials and API keys with automated renewal capabilities
- Phase 3: Certificate-based authentication systems with integrated certificate management
- Phase 4: Legacy system integration and custom applications requiring manual coordination
Expected Outcome: Achieve 95%+ automated credential rotation while reducing manual credential management overhead by approximately 75%.
Step 9: Deploy EDR/XDR with Credential Monitoring
Priority: High | Implementation Time: 1-3 days | ROI: Very High
Extended Detection and Response platforms provide comprehensive visibility into credential usage patterns and detect abnormal access behaviors that may indicate compromise or unauthorized usage across endpoint and network environments.
Leading Solutions for SMBs
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Comprehensive endpoint security with integrated credential monitoring capabilities
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Cloud-native platform with real-time threat intelligence and advanced credential abuse detection
- SentinelOne Singularity: AI-driven endpoint protection with autonomous response capabilities and behavior analysis
- Sophos Intercept X: Multi-layered defense combining EDR and XDR with anti-ransomware features
Credential-Specific Monitoring
- Privileged Account Activity: Monitor administrative credential usage across systems with behavior baselines
- Service Account Behavior: Detect anomalous patterns in automated system access and unusual authentication attempts
- Remote Access Monitoring: Track VPN and remote desktop credential usage with geographic and temporal analysis
- Cloud Console Access: Monitor administrative access to cloud management interfaces with session analysis
Integration Requirements
- SIEM integration for centralized logging, correlation, and comprehensive event analysis
- Identity provider integration for user context, risk scoring, and behavioral profiling
- Vulnerability management integration for risk-based prioritization and threat contextualization
- Incident response automation for rapid containment, investigation, and remediation workflows
Expected Outcome: Reduce credential-based attack detection time from days to minutes while enabling automated response to suspicious activity patterns. This monitoring capability integrates effectively with broader cybersecurity frameworks for comprehensive threat detection and response.
Step 10: Conduct Regular Secrets Audits
Priority: Medium | Implementation Time: 4-8 hours monthly | ROI: High
Regular auditing ensures comprehensive coverage while identifying gaps in existing security measures and providing quantifiable metrics for continuous improvement and compliance demonstration.
Audit Scope and Frequency
- Weekly: Repository scanning results review and remediation status tracking
- Monthly: Comprehensive infrastructure credential inventory and risk assessment
- Quarterly: Access review, privilege validation, and policy compliance verification
- Annually: Complete security architecture assessment and strategic planning review
Audit Methodology
- Automated Discovery: Use comprehensive scanning tools to identify all credential storage locations
- Manual Validation: Verify automated findings and identify edge cases requiring human analysis
- Risk Assessment: Prioritize findings based on access level, system criticality, and business impact
- Remediation Planning: Create detailed action plans with clear timelines and ownership assignments
- Trend Analysis: Track improvement metrics and identify recurring issues for systematic resolution
Audit Tools and Integration
- GitGuardian Perimeter Monitoring: Public exposure scanning across multiple platforms and repositories
- Shodan/Censys: Internet-facing service credential exposure detection and monitoring
- Custom Scripts: Organization-specific patterns and legacy system integration requirements
- Compliance Frameworks: NIST, SOC 2, ISO 27001 mapping for regulatory requirements and certification
Expected Outcome: Maintain comprehensive visibility into credential exposure while demonstrating continuous improvement in security posture metrics. Regular auditing aligns with comprehensive security assessment practices for ongoing security improvement and compliance maintenance.
Implementation Roadmap and Prioritization
Immediate Actions (Week 1)
Focus: Establish baseline protection against credential exposure
- Enable repository scanning across all code management platforms with appropriate alert routing
- Implement pre-commit hooks for active development repositories and establish developer training
- Audit and systematically shorten token lifetimes for critical cloud services and databases
- Deploy honeytokens in high-visibility locations with comprehensive monitoring
Expected Impact: 60-80% reduction in new credential exposures across development workflows
Short-Term Implementation (Weeks 2-4)
Focus: Systematic coverage across all credential storage locations
- Complete SSO deployment for all SaaS applications with proper access controls
- Implement container image scanning in CI/CD pipelines with automated failure conditions
- Deploy EDR/XDR solution with comprehensive credential monitoring capabilities
- Begin collaboration platform monitoring deployment with platform-specific configurations
Expected Impact: 90%+ reduction in credential exposure across all systems and platforms
Long-Term Optimization (Months 2-6)
Focus: Automation and continuous improvement
- Implement comprehensive secrets rotation automation with health monitoring
- Establish regular audit processes with quantifiable improvement metrics
- Integrate all security tools for centralized monitoring and coordinated response
- Develop advanced threat hunting capabilities focused on credential abuse patterns
Expected Impact: Achieve enterprise-grade credential security with minimal ongoing operational overhead
Essential Tools and Solutions
Secrets Detection and Management
GitGuardian
GitGuardian offers comprehensive secrets detection across repositories, containers, and collaboration platforms. Their enterprise platform provides centralized visibility and automated remediation workflows, making it particularly suitable for organizations managing multiple development teams and complex infrastructure environments. The platform achieves 95% precision through machine learning-enhanced detection algorithms.
HashiCorp Vault / IBM Vault Radar
HashiCorp Vault serves as a leading solution for secrets management, offering dynamic secrets generation, automated rotation, and comprehensive audit logging. Following IBM's acquisition, IBM Vault Radar (for secret detection) is now priced at $7.00 per active user/month. The platform's extensive integration ecosystem suits organizations seeking to implement enterprise-grade secrets management practices with support for multiple cloud providers and databases.
AWS Secrets Manager
AWS Secrets Manager provides cloud-native secrets management with deep integration into AWS services. For organizations primarily operating within the AWS ecosystem, it offers seamless integration with IAM policies, automated rotation capabilities, and comprehensive logging through CloudTrail.
Identity and Access Management
Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID delivers comprehensive identity and access management with extensive SaaS integration capabilities. The platform's conditional access policies and security defaults suit organizations seeking enterprise-grade identity security. Explore Microsoft 365 Business Plans
1Password Business
For organizations seeking comprehensive password management with secrets sharing capabilities, 1Password Business provides enterprise-grade credential management with developer-friendly secret storage and sharing features designed for technical teams.
Endpoint Detection and Response
EDR/XDR Solutions
- CrowdStrike Falcon: Cloud-native endpoint security with real-time threat intelligence and advanced credential monitoring capabilities
- SentinelOne Singularity: AI-driven endpoint protection with autonomous response capabilities and behavior analysis
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: Comprehensive endpoint security with deep integration into Microsoft ecosystems
- Acronis Cyber Protect: Combined endpoint protection with comprehensive data backup and recovery capabilities
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Key Performance Indicators
Detection Metrics
- Mean time to detect credential exposure (target: under 15 minutes)
- Percentage of secrets prevented before repository commit (target: 95% or higher)
- False positive rate in detection systems (target: under 5%)
- Coverage percentage across all credential storage locations (target: 100%)
Response Metrics
- Mean time to remediate exposed credentials (target: under 4 hours)
- Percentage of automated remediation versus manual intervention (target: 80% or higher)
- Incident escalation rate for credential exposure events (target: under 10%)
- User compliance rate with security procedures (target: 95% or higher)
Business Impact Metrics
- Reduction in security incidents involving compromised credentials (target: 90% or higher)
- Improvement in security audit scores and compliance ratings
- Reduction in developer productivity impact from security procedures (target: minimal)
- Cost savings from prevented incidents and improved operational efficiency
Continuous Improvement Framework
Monthly Reviews:
- Analyze detection accuracy and tune scanning tools based on performance data
- Review remediation procedures and identify optimization opportunities
- Update training materials based on emerging threats and tool updates
- Assess compliance with established procedures and identify procedural gaps
Quarterly Assessments:
- Conduct comprehensive security architecture review with stakeholder input
- Update threat modeling based on infrastructure changes and new threat intelligence
- Perform vendor assessment and tool evaluation for emerging capabilities
- Complete cost-benefit analysis of security investments and tool consolidation opportunities
Annual Strategic Planning:
- Execute complete security posture assessment against industry benchmarks
- Develop technology roadmap planning for emerging threats and capabilities
- Plan team training and certification requirements for the coming year
- Conduct comprehensive budget planning and resource allocation optimization
Common Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Developer Adoption and Training
Challenge: Resistance to new security procedures that may impact development velocity or workflows
Solution: Implement security tools that integrate seamlessly into existing workflows while providing clear, demonstrable value to developers. Focus on automation that reduces manual work rather than adding additional procedural steps. Provide comprehensive training that explains the business rationale and risk mitigation benefits.
Tool Integration and Compatibility
Challenge: Ensuring compatibility between multiple security tools and existing infrastructure components
Solution: Prioritize tools with strong API integration capabilities and established ecosystem partnerships. Implement solutions incrementally to identify and resolve compatibility issues before full deployment. Maintain clear documentation of all integrations, dependencies, and configuration requirements.
False Positive Management
Challenge: High false positive rates in secret detection leading to alert fatigue and reduced effectiveness
Solution: Invest adequate time in proper tool configuration and baseline establishment. Implement tiered alerting based on risk levels and confidence scores. Regularly tune detection rules based on organizational patterns and feedback from both security and development teams.
Cost and Resource Management
Challenge: Balancing security requirements with budget constraints and limited personnel resources
Solution: Focus on high-impact automation that reduces long-term operational overhead. Prioritize tools that consolidate multiple security functions rather than specialized point solutions. Consider managed services for complex capabilities that require specialized expertise or 24/7 monitoring.
The Business Case for Comprehensive Secrets Hygiene
Risk Reduction and Investment Analysis
With data breaches now costing U.S. businesses an average of $10.22 million (while the global average dropped to $4.44 million in 2025), implementing comprehensive secrets hygiene practices delivers measurable risk reduction across multiple organizational dimensions. The divergence between U.S. and global costs highlights how regulatory and legal environments amplify financial exposure domestically. For SMBs, preventing even a single credential-based breach can save millions in direct costs, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
Organizations with mature secret detection capabilities typically experience substantial reductions in credential-related security incidents within the first year of implementation. The comprehensive approach outlined in this checklist typically requires annual investments ranging from $40,000-$150,000 for mid-sized organizations, depending on existing infrastructure and chosen solution providers—a fraction of the potential breach cost.
The operational efficiency gains often justify significant portions of this investment independently. Organizations with comprehensive incident response capabilities can reduce breach detection and containment timelines substantially, translating to significant cost savings and reduced business disruption. Additionally, automated secrets management reduces manual credential management overhead by approximately 75%, freeing development and operations teams for value-creating activities.
Competitive Advantage and Trust Building
Organizations demonstrating mature security practices gain measurable competitive advantages in customer acquisition and retention scenarios. Security certifications and compliance achievements enabled by comprehensive secrets management often become explicit requirements for enterprise sales cycles and partnership opportunities, directly impacting revenue potential.
Regulatory Compliance and Insurance Benefits
Comprehensive secrets hygiene practices directly support compliance with regulations including GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and industry-specific requirements. These implementations often qualify organizations for reduced cyber insurance premiums while ensuring coverage requirements are met during incident response scenarios and claims processes.
Get Your Free Security AssessmentFrequently Asked Questions
How quickly can these measures be implemented in a typical SMB environment?
Most organizations can implement the critical first four steps within 1-2 weeks. Repository scanning and pre-commit hooks can be deployed within days, while SSO implementation typically requires 3-5 business days depending on the number of applications. Complete implementation of all ten steps usually takes 2-3 months, depending on organizational complexity and existing infrastructure.
What are the typical costs for implementing comprehensive secrets management?
For most SMBs (25-100 employees), comprehensive secrets management tools typically cost $12,000-$60,000 annually. Key 2026 pricing includes: GitHub Secret Protection at $19 per active committer/month, IBM Vault Radar at $7 per active user/month, plus identity management and endpoint detection platforms. Given the average U.S. breach cost of $10.22 million (global: $4.44M), organizations typically achieve positive ROI within 6-12 months through prevented incidents and operational efficiency gains.
Will these security measures impact development team productivity?
When implemented properly, these measures actually improve development velocity by eliminating manual security tasks and reducing incident response overhead. Pre-commit hooks add 2-5 seconds to commit operations, while automated secrets management eliminates hours of manual credential rotation work and reduces security-related development delays.
How do we handle legacy systems that cannot integrate with modern secrets management?
Legacy systems require hybrid approaches including network segmentation, privileged access management, and enhanced monitoring. Many organizations use jump servers or privileged access workstations to provide secure access to legacy systems while maintaining comprehensive audit trails and centralized credential management for supported systems.
What should we do if we discover credentials that have already been exposed publicly?
Immediate rotation is essential, followed by comprehensive impact assessment. Most platforms provide automated notification when their credentials are compromised. Organizations should assume that exposed credentials have been compromised and plan remediation accordingly, including potential forensic analysis for high-value systems and thorough access log review.
How often should secrets be rotated in different environments?
Development environments should use credentials with 1-24 hour lifetimes, production databases should rotate weekly to monthly, and administrative accounts should rotate monthly to quarterly. API keys should generally rotate every 30-90 days, while certificates typically have 1-year maximum lifetimes with automated renewal processes.
How do we protect against AI-driven credential exposure?
With 65% of leading AI companies having leaked verified secrets, organizations must implement AI-specific security controls: (1) Deploy AI usage policies prohibiting code sharing with external LLMs, (2) Implement AI gateway solutions that scan and redact credentials before LLM submission, (3) Train developers to sanitize code before pasting into ChatGPT, Claude, or Copilot Chat, (4) Monitor for prompt injection attacks attempting credential extraction, and (5) Use "Developer-in-the-loop" workflows that flag potential AI-related exposures. Treat all AI tools as untrusted third parties requiring the same security controls as external contractors.
Related Resources
- Best Business Password Managers – Credential management
- Best Cybersecurity Software for Small Business – Security tools
- NIST CSF 2.0 Cybersecurity Tools – Framework implementation
- Small Business Network Security Audit Guide – Security audits
- Small Business Security Assessment Guide – Free assessment
- GitHub Malware Security Guide – Repository threats
- Cybersecurity Services – Professional support
Related Articles
More from Cybersecurity

AI Agent & Service Account Security for SMBs: 2026 Comprehensive Playbook
Complete SMB playbook for securing AI agents and service accounts. Governance frameworks, platform comparisons (Entra ID, Google Cloud IAM, Okta), and step-by-step implementation guide.
16 min read

The True Cost of Employees Sharing Passwords in Spreadsheets
Password spreadsheets cost businesses millions in breaches. Learn the hidden financial risks of shared credentials and how to protect your company.
13 min read

Best Password Manager for Small Business 2026: Admin-Focused Comparison
Compare Proton Pass, 1Password, NordPass & Bitwarden for real-world business deployment. Admin controls, team management, offboarding, and pricing that scales.
27 min read
