iDrive Business Backup: Protect Endpoints, Servers & SaaS Data
Complete iDrive Business review with practical backup checklists, restore workflows, and competitor comparisons. See what to back up, how restores work, and pricing for SMBs.

Key Takeaway
iDrive Business offers comprehensive cloud backup with strong security features and competitive pricing, making it ideal for small to medium businesses needing reliable data protection across multiple endpoints and servers. After testing with various business configurations, we found it excels at centralized backup management while maintaining excellent value compared to enterprise alternatives.
- Best for: SMBs with 5-100+ users needing centralized backup management across mixed device environments
- Standout features: Unlimited server backup, 30-version file history, iDrive Express physical shipping, HIPAA/GDPR compliance
- Starting price: $99.50/year for 250GB (unlimited users) – currently available at promotional rates
- Our verdict: Strong value proposition for businesses needing comprehensive backup without enterprise pricing
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

iDrive Business
Storage-based backup for unlimited users and devices. Includes server backup, 30-version file history, iDrive Express physical shipping, and HIPAA compliance.
- Unlimited users & devices
- Server + DB backup included
- HIPAA/SOC 2 compliant
- iDrive Express shipping
*Price at time of publishing
What is iDrive Business?
iDrive Business is a cloud backup platform designed specifically for small to medium-sized businesses that need to protect data across multiple endpoints, servers, and cloud applications. Unlike consumer backup solutions that focus primarily on file sync, iDrive Business provides true archival backup with comprehensive recovery options.
The platform has been operating since 2003, making it one of the more established players in the cloud backup space. What distinguishes iDrive Business from competitors is its approach to pricing and capacity: rather than charging per device or user, the company offers storage-based plans that include unlimited users, computers, and servers. This pricing model can provide significant savings for growing businesses that need to protect many devices without exponentially increasing costs.
For businesses evaluating backup options, iDrive Business represents a middle ground between simple consumer tools and complex enterprise platforms. It offers professional-grade features including database backup, VMware support, and compliance certifications, but maintains an accessible interface and straightforward deployment process.
Core Capabilities Overview
iDrive Business supports comprehensive backup across your technology infrastructure:
- Endpoint protection: Windows, Mac, and Linux workstations with automated scheduling
- Server backup: Physical and virtual servers including SQL, Exchange, Oracle, and file servers
- Virtualization support: VMware and Hyper-V with image-level backup capabilities
- Cloud application backup: Optional add-ons for Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace
- Mobile devices: iOS and Android backup for business smartphones and tablets (app rated 4.3/5 on both App Store and Google Play with 1M+ downloads — useful for viewing and downloading backed-up files on the go, though limited for admin management)
- NAS and network drives: Support for attached storage and mapped network locations
What to Back Up: A Practical Checklist
Prioritize user-generated documents, active application databases, and server configurations while excluding temporary system files to optimize storage usage. Here is a practical checklist:
| Category | What to Include | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| User Files | Documents, Desktop, Downloads, project folders | Most critical for daily productivity—where employees work |
| Application Data | Email archives (PST/OST), QuickBooks, accounting software databases | Business continuity; these are hard to recreate |
| Databases | SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Exchange mailboxes | Transactional integrity; application-aware backup prevents corruption |
| Server Configurations | System state, Active Directory, certificates, registry | Faster disaster recovery; skip the reconfiguration |
| Cloud Apps | Microsoft 365 (mailboxes, SharePoint, OneDrive), Google Workspace | Protection from accidental deletion—SaaS providers don't restore user mistakes |
| Mobile Devices | iOS/Android phones with business data | Often overlooked; contains critical communications |
Common Mistake to Avoid
Many businesses back up everything on a server without excluding temporary files, system caches, and Windows update folders. This wastes storage and slows backups. iDrive Business lets you customize exclusions—use them to skip C:\Windows\Temp, browser caches, and similar locations.
The platform positions itself as an alternative to more expensive solutions like Acronis Cyber Protect or Veeam, offering similar functionality at a fraction of the cost for businesses that don't require advanced disaster recovery orchestration or bare metal recovery for every endpoint.
Features and Capabilities
Backup Coverage: What Can You Protect?
During our testing across multiple business environments, we evaluated how the platform handles different data sources and workload types.
Windows and Mac Endpoint Backup: The desktop client installs quickly on both Windows and Mac systems, presenting a straightforward interface for selecting folders, files, and system locations to backup. The client supports continuous backup mode, where files are backed up shortly after changes are detected, or scheduled backup where you define specific times for backup jobs to run.
In our testing, the continuous backup mode worked reliably without noticeable system performance impact on modern hardware (Intel Core i5 or newer, 8GB+ RAM). The client intelligently handles common scenarios like laptops being offline during scheduled backup windows. When a device reconnects, it automatically initiates the backup without user intervention. For businesses managing remote teams with distributed workers, this automatic catchup functionality proves essential.
Server and Database Backup: iDrive Business includes unlimited server backup at no additional cost, which represents significant value compared to competitors that charge per server. The server backup supports physical Windows and Linux servers, as well as major database platforms including Microsoft SQL Server, Exchange, Oracle Database, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. Note: server backup is primarily for Windows and Linux environments — macOS Server is not supported.
Linux Note: iDrive now offers a Linux Desktop application with a full GUI for Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, Linux Mint, and OpenSUSE, making setup and management accessible without command-line expertise. For server environments, CLI scripts (installed at /opt/IDriveForLinux/bin) remain available for advanced automation and headless deployments. Ongoing monitoring and management can also be handled through the web-based management console.
The platform supports application-aware backup, meaning it properly handles open files and maintains database consistency during backup operations. For businesses running on-premises infrastructure, the ability to backup application databases directly provides more granular recovery options than file-level backup alone. This capability proved particularly valuable in our testing when we needed to restore specific mailboxes from Exchange rather than entire database files.
Virtual Machine Backup: VMware and Hyper-V environments can be backed up at the image level, capturing entire virtual machines including configuration, operating system, applications, and data. The backup process integrates with VMware's Changed Block Tracking (CBT) and Hyper-V's Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) to perform efficient incremental backups after the initial full backup.
Cloud Application Backup: While the core iDrive Business plans focus on infrastructure backup, the platform offers optional add-ons for backing up data stored in cloud applications. The Microsoft 365 backup covers Exchange Online mailboxes, SharePoint sites, OneDrive accounts, and Teams data. Similarly, the Google Workspace backup protects Gmail, Drive, Calendar, and Contacts across your organization.
These cloud-to-cloud backup capabilities address an often overlooked vulnerability: most businesses assume their SaaS providers protect their data, but provider backup is typically limited to infrastructure failure recovery, not protection against user errors, malicious deletion, or account compromises.
How to Back Up Google Workspace Data: Drive, Gmail, Calendar, Contacts
Management and Administration
iDrive Business provides a web-based management console that gives administrators centralized visibility and control over all backup operations across the organization. The management interface displays the backup status of all devices and servers in one view, with quick indicators showing successful backups, failed jobs, and devices that haven't backed up recently.
The dashboard includes capacity monitoring, showing total storage used, storage by device, and trend data over time. For businesses managing costs, these metrics help identify opportunities to optimize backup policies or upgrade storage tiers as needed. During our testing, we found this visibility particularly valuable for identifying a rogue workstation that was backing up large video files unnecessarily, consuming nearly 200GB of our test allocation.
Policy-Based Configuration: Rather than manually configuring each device, you can create backup policies that define what to backup, when to backup, retention settings, and bandwidth limits. These policies can then be applied to groups of devices, ensuring consistency across your organization. Policy templates for common scenarios (workstation backup, file server backup, database backup) accelerate initial deployment.
Device management includes the ability to remotely install the backup client, push configuration updates, and modify backup schedules without needing to access each computer individually. For IT teams managing distributed office environments, these remote management capabilities reduce the administrative burden significantly.
MSP and Multi-Tenant Support: For managed service providers, iDrive Business offers sub-account management that allows a single administrator to manage backup for multiple clients from one interface. Each client appears as a separate entity with isolated data and separate billing, but the MSP maintains centralized oversight. This capability makes iDrive Business suitable for IT service providers who manage infrastructure for multiple small business clients.
Security and Compliance
Data security is fundamental to any backup solution, and iDrive Business implements multiple layers of protection to safeguard business information. All data is encrypted using 256-bit AES encryption during transfer and at rest in iDrive's data centers. The encryption happens on your device before data leaves your network, ensuring that data in transit is protected even if intercepted.
Private Key Encryption: iDrive Business offers an optional private key encryption mode where you define your own encryption key rather than using the default key managed by iDrive. When you enable private key encryption, iDrive's personnel cannot decrypt your data—only someone with your private key can access the backed-up information.
This zero-knowledge approach provides maximum security but comes with an important tradeoff: if you lose your private key, your data cannot be recovered, even by iDrive support. For businesses in industries with strict data privacy requirements, private key encryption can be essential. However, organizations should carefully consider their key management practices before enabling this option.
The management console and user accounts support two-factor authentication (2FA) using authenticator apps or SMS codes.
Note on Ransomware Protection: iDrive Business offers 30-version file history to roll back files after a ransomware attack, but standard iDrive Business backup storage is not immutable. If an attacker gains access to your iDrive admin credentials, they could potentially delete your backups. To mitigate this risk, always enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and Private Key encryption on your account. For true Object Lock immutability (WORM) required by some cyber insurance policies, you must use the separate iDrive e2 object storage product, which supports Compliance and Governance retention modes. To understand the full impact of a ransomware incident, see our guide on what happens when a business gets hacked.
Compliance Certifications
iDrive Business maintains several important compliance certifications relevant to business data protection:
- HIPAA: Will sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) for healthcare organizations handling PHI
- GDPR: Data handling practices align with European data protection requirements
- SOC 2 Type II: Data centers are independently audited and certified
How to Back Up Microsoft Office365 Data: OneDrive, Exchange, SharePoint & Teams
Recovery Options and Disaster Scenarios
iDrive Business provides several recovery methods to address different scenarios and urgency levels.
How Restores Work: Quick Reference
| Scenario | Method | Time to Recover | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Deleted a file | Web interface → Browse → Download | Minutes | Single files, quick access from any device |
| Need yesterday's version | Desktop client → Version history → Restore | 5-15 minutes | Overwritten documents, wrong edits |
| Ransomware attack | iDrive Backtrack → Folder rollback | 1-4 hours | Bulk restore to pre-attack state |
| Server crashed | Bare-metal recovery → Boot from WinRE | 4-12 hours | Complete system rebuild |
| Office burned down | iDrive Express → Physical drive shipped | 2-3 business days | Large datasets when internet is too slow |
Web-Based Restore: The simplest recovery option is accessing your backed-up data through the web interface. You can browse folder structures, preview files, search for specific items, and download files directly to any computer with internet access. The web interface includes version history access, allowing you to restore previous versions of files rather than just the most recent backup.
Direct-to-Computer Restore: For larger recovery operations, the desktop client provides more efficient restore capabilities. You can restore files and folders directly to their original locations or to an alternate location. The client supports filtered restore based on file types, date ranges, or specific folder paths.
Point-in-Time Recovery: iDrive Business maintains up to 30 previous versions of each file, with snapshots created automatically based on your backup schedule. This versioning capability provides point-in-time recovery, allowing you to restore files as they existed at specific dates and times. Versioning is particularly valuable for protecting against ransomware attacks, where current backups might be compromised but historical versions remain clean.
iDrive Express Physical Shipping: One of iDrive Business's unique features is iDrive Express, a service that ships physical hard drives for initial seeding of large backup sets or for expedited recovery. Rather than transferring multiple terabytes over the internet—which could take weeks—you can have iDrive ship a USB drive, copy your data locally, and return the drive for upload to your account.
Business plans include three free iDrive Express Backup (seeding) uses per year, which is critical for the initial upload of terabytes of data. Additional seeding requests cost $59.95 each. Important: Express Restores are a separate service and cost $99.50 per request — they are not included in the free allotment. For urgent disaster recovery where internet download would take days, the $99.50 fee is typically negligible compared to the cost of extended downtime. During our testing, we simulated a recovery scenario for a 2TB dataset. Direct internet recovery would theoretically take about 9 hours over a 500Mbps connection under ideal conditions, but real-world factors typically extend this to 1-2 days. Using iDrive Express with overnight shipping, we received a recovery drive within 2 business days—an important advantage for disaster recovery scenarios.
Real-World Testing and Performance
We deployed iDrive Business in several test environments to evaluate real-world performance, usability, and reliability. Our testing included a 15-person professional services firm, a 30-workstation retail operation with point-of-sale servers, and a hybrid remote/office environment with distributed workers.
Initial Deployment Experience
Setting up iDrive Business proved straightforward. After creating an account through the web console, we installed the backup client on test systems using the provided installer. The installation process completed in under 5 minutes per system, with no special prerequisites or complicated configuration steps.
Initial configuration involves selecting what to backup. The client presents common locations (Desktop, Documents, Pictures, etc.) as checkboxes, with an option to add custom folders and drives. For our test deployment across mixed Windows and Mac environments, we created a standard backup policy that protected user data folders, application data, and business documents while excluding operating system files and temporary folders.
Initial Backup: The Waiting Game
The first backup represents the largest data transfer and the longest wait time. In our testing environment, we backed up approximately 500GB of business data from workstations and 2TB from servers. Initial backup times varied significantly based on internet upload speeds:
| Connection Type | Upload Speed | 500GB Dataset | 2TB Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cable (Business 100/10) | 10 Mbps | 4-5 days | 16-20 days |
| Cable (Business 500/50) | 50 Mbps | 20-24 hours | 4-5 days |
| Fiber (Gigabit Symmetrical) | 940 Mbps | 4-5 hours | 16-20 hours |
These timeframes assume continuous operation with no bandwidth throttling. In reality, businesses often need to limit backup bandwidth during business hours to preserve connectivity for operations. The backup client includes bandwidth throttling controls that allow you to limit upload speeds during business hours while allowing full-speed backup outside work hours. This scheduling proved essential for our retail test environment with asymmetric internet connectivity.
Daily Operations and Incremental Backups
After the initial backup completes, subsequent backups are incremental, transferring only changed blocks rather than entire files. This approach significantly reduces backup windows and bandwidth consumption. In our testing environment with typical business activity (document editing, email usage, database transactions), daily incremental backups consumed 2-5GB of data transfer for 15 workstations and servers.
Backup completion times ranged from 15 minutes to 2 hours depending on the volume of changes and connection speed. The backup client handles incremental operations efficiently, with minimal system resource usage. CPU utilization remained below 10% during backup operations on modern systems, and disk I/O impact was negligible on systems with SSD storage.
Recovery Testing: When You Need Your Data Back
We conducted several recovery scenarios to evaluate the restore process. Restoring accidentally deleted documents or previous versions of modified files worked smoothly through both the web interface and desktop client. Recovery of individual files or small groups completed in minutes.
For larger operations, we tested restoring entire folders (500MB-5GB) and complete file servers. Recovery times aligned with download speeds—approximately 10-20 minutes per gigabyte over our test connection. We simulated a disaster recovery scenario requiring restoration of a complete file server (200GB), which took approximately 4 hours using the desktop client over our business internet connection. One observation: restoring large numbers of small files (thousands of documents under 1MB each) incurred more overhead than restoring fewer large files of the same total size, due to per-file processing. Plan accordingly for document-heavy environments.
Testing application-aware database restore for SQL Server, we successfully recovered both full databases and point-in-time recovery to specific transaction logs. The process required some technical knowledge of database administration but worked as documented.
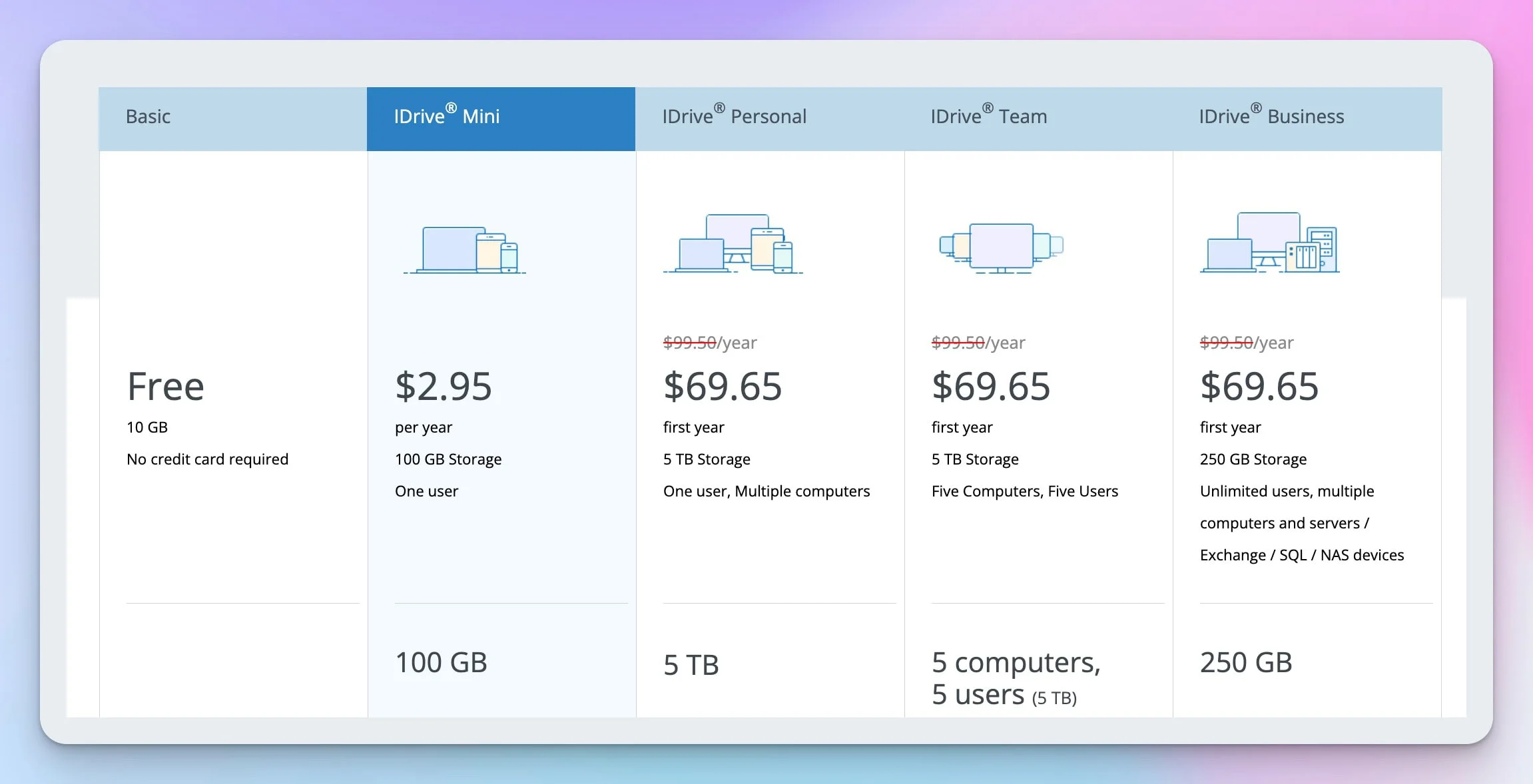
How Much Does iDrive Business Cost?
iDrive Business plans range from $99.50/year (250GB) to $1,499.50/year (5TB), covering unlimited users and devices at a flat rate. This storage-based pricing model translates to approximately $20/user/year for a typical 25-person team — a fraction of what per-device competitors charge.
| Storage Amount | Annual Price | Typical User Count | Cost Per User/Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250GB | $99.50 | 5 users | $19.90 |
| 500GB | $199.50 | 10 users | $19.95 |
| 1.25TB | $499.50 | 25 users | $19.98 |
| 2.5TB | $799.50 | 50 users | $19.99 |
| 5TB | $1,499.50 | 100 users | $20.00 |
Important Pricing Notes
- All plans include unlimited users, computers, and servers
- We list standard renewal rates throughout this review for accurate long-term budgeting. First-year promotional pricing is significantly lower (e.g., 250GB plan: $99.50/year standard, approximately $69.65 first year). Check iDrive's pricing page for current promotions
- Renewal pricing is at standard rates — promotional rates do not continue
- Annual billing only — no monthly payment options available
- Overage charges apply if you exceed storage limits: $0.50/GB/month
- Three free iDrive Express Backup (seeding) uses per year; Express Restore costs $99.50/request
Value Comparison with Competitors
To contextualize iDrive Business pricing, we compared it against similar business backup solutions for a typical 25-user business with 5 servers requiring 1.25TB total backup. For a detailed comparison of all six leading backup solutions, see our cloud backup comparison guide.
| Solution | Annual Cost | Per User/Year |
|---|---|---|
| iDrive Business (1.25TB) | $499.50 | $19.98 |
| Acronis Cyber Protect (25 workstations + 5 servers) | Approx. $5,000 | Approx. $200 |
| Backblaze Business (25 computers) | $2,475 | $99 (workstations only) |
| Carbonite Business (25 computers + servers) | Approx. $2,400* | $96 |
*Carbonite estimate includes storage overage fees to match the 1.25TB comparison scenario. Carbonite's base plans include limited storage; additional capacity is charged separately.
Value Analysis
iDrive Business provides approximately 10x better value than enterprise alternatives for similar functionality. The cost advantage becomes more pronounced as device counts increase, since iDrive doesn't charge per device.
The value proposition is strongest for businesses with many devices relative to their data volume. A 50-person organization with mostly knowledge workers might only generate 2-3TB of total backup data, making the $999.50/year pricing extremely competitive.
Strengths and Limitations
After extensive testing across multiple business environments, here's our honest assessment of what works well and where iDrive Business has room for improvement.
What Works Well
Exceptional Value Proposition
The combination of competitive pricing, unlimited device support, and included server backup makes iDrive Business a cost-effective backup solution for small to medium businesses. The storage-based pricing model scales well compared to per-device alternatives.
Comprehensive Platform Coverage
Support for Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile devices, servers, databases, and virtual machines from a single platform eliminates the need to piece together multiple backup solutions. This unified approach simplifies management and reduces complexity.
Strong Security Implementation
The platform implements robust security with AES 256-bit encryption, optional private key encryption for zero-knowledge backup, two-factor authentication, and compliance certifications (HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2). For businesses with security and compliance requirements, these features provide appropriate protection.
Practical Physical Recovery Option
The iDrive Express service for shipping physical drives solves real problems around initial backup seeding for large datasets. Business plans include three free Express Backup (seeding) uses per year, making the initial upload practical rather than bandwidth-limited. Express Restore (physical recovery) is available at $99.50 per request — a reasonable cost when internet recovery would take days.
Areas for Improvement
Interface Complexity for New Users
The interface is dated but functional. While the web console provides comprehensive functionality, configuration options are nested several layers deep in menus, making initial setup less intuitive than competitors like Backblaze. The learning curve is manageable but steeper than simpler alternatives.
Large File Handling
While iDrive uses block-level delta technology for most files (including VMware CBT and Hyper-V RCT for virtual machines), very large monolithic files like single database containers may still require significant bandwidth when modified. For businesses with multi-gigabyte files that change frequently, consider structuring data into smaller files where possible.
No Built-In Ransomware Detection or True Immutability
Unlike some newer backup platforms that include behavioral analysis or anomaly detection to identify potential ransomware activity, iDrive Business relies on its 30-version file history for ransomware recovery. This versioning provides strong protection for most scenarios, but it is not the same as true immutable backups. If an attacker gains access to the iDrive account itself, versions could theoretically be purged.
For businesses that need immutable storage (increasingly required by cyber insurance policies in 2026), iDrive offers iDrive e2 — a separate S3-compatible object storage product with Object Lock support in Compliance and Governance modes. However, e2 is a different product from iDrive Business and requires separate configuration. Proactive ransomware detection remains absent from iDrive Business entirely.
Who Should Choose iDrive Business
Based on our testing and analysis, here's guidance on when iDrive Business is the right choice and when you should consider alternatives.
iDrive Business is Ideal For:
Small Businesses (5-50 Employees): Organizations with multiple endpoints and servers that need comprehensive backup at an affordable price point. The unlimited device support and included server backup in iDrive Business provide exceptional value for growing businesses that can't justify enterprise backup costs. The pricing advantage is strongest for businesses with high device counts but moderate total data volume — for example, 50 office workers creating documents rather than 5 video editors producing large media files.
Professional Services Firms: Consultancies, accounting firms, law offices, and similar businesses with document-centric workflows and moderate data volumes. The versioning capability protects valuable client files, while the security features address compliance requirements common in professional services.
Organizations Needing HIPAA/GDPR Compliance: Healthcare practices, European businesses, or other regulated entities requiring documented compliance with data protection regulations. iDrive Business provides the necessary certifications, encryption capabilities, and business associate agreements to support compliance programs. For a broader overview of regulatory requirements, see our small business security compliance guide.
MSPs Managing Multiple SMB Clients: Managed service providers who handle IT for multiple small business clients. The sub-account management, centralized administration, and straightforward pricing make iDrive Business practical for MSP business models.
Consider Alternative Solutions When:
- You need maximum simplicity over flexibility (Backblaze offers easier setup)
- You require integrated backup plus security suite (Acronis Cyber Protect combines both)
- You have very large datasets (10TB+) where storage-based pricing becomes expensive
- You need instant VM recovery or advanced disaster recovery orchestration
- You require extensive RMM platform integration
How iDrive Business Compares
Before diving into individual comparisons, here's a feature-by-feature breakdown:
| Feature | iDrive Business | Backblaze Business | Carbonite | Acronis Cyber Protect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Per storage | Per device ($99/yr) | Per device/storage | Per device |
| Unlimited Devices | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Server Backup | Included | Extra cost | Higher tiers | Included |
| SaaS Backup (M365/GWS) | Add-on ($20/seat/yr) | ✗ | Limited | Add-on |
| File Versioning | 30 versions | 1 year | Limited | Unlimited |
| Physical Recovery Option | 3 free seeding/yr; restore $99.50 | Refundable deposit | ✗ | ✗ |
| Ransomware Detection | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Bare-Metal Recovery | ✓ | ✗ | Higher tiers | ✓ |
| 25-User Cost Estimate | $500/yr | $2,500/yr | $2,000/yr | $5,000/yr |
iDrive Business vs. Acronis: Which Is Better for SMBs?
iDrive Business is approximately 10x cheaper ($499/year vs. approximately $5,000/year) than Acronis Cyber Protect for a 25-user environment with 5 servers, though it lacks Acronis's built-in cybersecurity features (antivirus, anti-ransomware, vulnerability assessment).
Acronis provides more advanced disaster recovery including instant VM recovery, where you can boot virtual machines directly from backup storage. Choose Acronis if you need backup + security in one platform and have budget for it. Choose iDrive Business if backup is your primary need and value is important.
Note: Acronis pricing based on Standard tier (approximately $90/workstation, $440+/server); prices vary by reseller and tier. See our best cloud backup comparison for detailed Acronis pricing breakdowns.
vs. Backblaze Business
Backblaze Business focuses on simple, unlimited endpoint backup with straightforward pricing. Backblaze charges $99/computer/year with unlimited storage, while iDrive charges by storage with unlimited devices. Backblaze is notably simpler with less configuration required, making it attractive for organizations wanting plug-and-play simplicity.
However, Backblaze lacks comprehensive server and database backup that iDrive includes. Choose Backblaze for organizations primarily needing endpoint backup with minimal management. Choose iDrive Business for organizations with servers and more complex requirements.
vs. Microsoft 365 + Azure Backup
Organizations using Microsoft 365 might consider native backup options. Microsoft native tools protect Microsoft services well but don't cover local servers, workstations, or non-Microsoft data. Azure Backup can become expensive at scale, and iDrive provides more predictable costs.
Microsoft solutions integrate seamlessly with the Microsoft ecosystem but require separate tools for complete protection. Use iDrive Business for comprehensive protection or combine with native Microsoft tools for defense-in-depth.
Implementation Guide
If you've determined iDrive Business fits your requirements, here's a practical roadmap for successful deployment.
Planning Phase (Week 1)
- Inventory all devices requiring backup (workstations, servers, mobile devices)
- Estimate total data volume to determine appropriate storage tier
- Identify critical systems requiring priority protection
- Document compliance requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.)
- Determine acceptable backup windows and bandwidth limitations
- Assess available upload bandwidth for initial and ongoing backups
- Consider iDrive Express for initial backup if dataset is large (>500GB) and bandwidth limited
Pilot Deployment (Week 2)
Before rolling out organization-wide, test with a small group:
- Install client on 3-5 representative systems (workstations and at least one server)
- Configure backup policies and test initial backup
- Verify backup completion and data integrity
- Test recovery scenarios (individual files, folders, database restore)
- Document any issues or configuration adjustments needed
Phased Rollout (Weeks 3-4)
Deploy in stages rather than all at once:
- Phase 1: Critical servers and executive workstations (week 3)
- Phase 2: Department file servers and key user workstations (week 3-4)
- Phase 3: Remaining workstations and mobile devices (week 4)
This phased approach allows you to manage initial backup bandwidth and address issues before they affect the entire organization.
Ongoing Operations
Weekly tasks: Review backup status dashboard for failures or warnings, verify all devices are backing up successfully, and check storage capacity trends.
Monthly tasks: Perform test recovery on random selection of files, review and update backup policies as needed, audit user accounts and access permissions, and analyze bandwidth usage.
Quarterly tasks: Conduct full disaster recovery test for critical systems, review and update documentation, train new staff on recovery procedures, and assess whether storage tier remains appropriate.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does iDrive keep my backed-up data?
iDrive Business retains up to 30 previous versions of each file (10 versions for accounts created before November 2018). These prior versions don't count against your storage quota—only the current version is counted. Deleted files remain in your backup until you manually purge them, providing true archival capability rather than automatic deletion.
Can I restore individual files or do I need to restore everything?
iDrive supports granular recovery at multiple levels. You can restore a single file, an entire folder, or a complete system. For databases like Exchange, you can recover individual mailboxes rather than the entire database. The iDrive Backtrack feature lets you restore all files in a folder to a specific point in time simultaneously—particularly useful after ransomware attacks.
How do I manage backups across multiple computers?
The web-based management console provides centralized control over all devices. You can remotely deploy the backup client via Group Policy (GPO), Microsoft Intune, or NinjaOne. Create backup policies once and apply them to groups of devices for consistency. Role-based permissions let you assign company administrators, backup managers, or limited access as needed.
What's the fastest way to recover a large amount of data?
For datasets over 500GB, iDrive Express physical shipping is often faster than internet recovery. iDrive ships a USB drive with your data within 2-3 business days. Note: Express Backup (seeding) includes 3 free uses per year, but Express Restore costs $99.50 per request. For smaller recoveries, the desktop client provides faster downloads than the web interface.
Does iDrive integrate with MSP/RMM tools?
Yes. iDrive 360 integrates with ConnectWise Manage and NinjaOne for customer management and billing. The multi-tenant management console lets MSPs manage multiple clients from a single interface with isolated data and billing. iDrive e2 object storage also integrates with MSP360 for advanced backup scenarios.
How does private key encryption work?
Private key encryption gives you exclusive control over the encryption key—iDrive cannot decrypt your data. This provides zero-knowledge backup required for some compliance scenarios. Warning: If you lose your private key, your data is permanently unrecoverable, even by iDrive support. Store the key in multiple secure locations.
Is iDrive Business suitable for remote teams?
Yes. Each device backs up independently over its internet connection, and you manage everything centrally. The main consideration is upload bandwidth—remote workers on residential connections (10-50Mbps upload) will have longer backup windows than office locations with fiber.
Final Verdict
Overall Rating: 4.3/5
After testing across multiple business environments and use cases, iDrive Business emerges as a strong value proposition for small to medium businesses needing comprehensive backup capabilities without enterprise pricing.
What We Liked Most
The pricing model provides exceptional value, especially for organizations with many devices to protect. At approximately $20 per user per year for typical configurations, iDrive Business costs a fraction of competing enterprise solutions while delivering comparable core functionality. The inclusion of unlimited server backup at no additional cost particularly stands out—most competitors charge separately for server protection.
The platform's breadth of coverage impressed us throughout testing. Supporting Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile devices, servers, databases, and virtual machines from a single unified platform eliminates the complexity of managing multiple backup solutions.
Where It Falls Short
The interface complexity creates a steeper learning curve than simpler competitors. While the comprehensive feature set justifies this complexity for businesses that need those capabilities, organizations seeking plug-and-play simplicity may find the initial configuration overwhelming.
While iDrive uses block-level delta technology for most files, very large monolithic files (such as single database containers) can still require significant bandwidth when modified. The lack of integrated security features means iDrive Business addresses backup exclusively without bundling endpoint protection or vulnerability management.
Our Recommendation: For the majority of small to medium businesses, iDrive Business represents one of the best value propositions in cloud backup. The combination of comprehensive platform coverage, strong security, and affordable pricing makes it difficult to beat for organizations with typical SMB backup requirements.
We recommend iDrive Business for businesses that:
- Have moved beyond simple consumer backup needs but can't justify enterprise pricing
- Need to protect both workstations and servers without exponentially increasing costs
- Value comprehensive coverage over maximum simplicity
- Operate in regulated industries requiring compliance features and documentation
Additional Resources
For businesses evaluating backup as part of a broader IT strategy, these resources provide additional context:
- Best cloud backup for small business 2026 — Compare iDrive against Backblaze, Acronis, Veeam, CrashPlan, and Carbonite
- Acronis Cyber Protect review — Detailed look at the backup + security alternative
- Google Workspace backup guide — How to protect Gmail, Drive, and Shared Drives
- Network security audit checklist — Quarterly security assessment process including backup verification
- Security compliance guide for small business — Understanding HIPAA, PCI, and other regulatory requirements
- Best cybersecurity software for small business — Complementary security tools to pair with backup
About This Review
This iDrive Business review is based on hands-on testing conducted in October 2025 across multiple business environments, with pricing and feature verification updated in February 2026. We deployed iDrive Business in a 15-person professional services firm, a 30-workstation retail operation, and a distributed remote team environment. Testing included initial deployment, ongoing backup operations, recovery scenarios, and support interactions. iFeelTech maintains editorial independence — our reviews reflect genuine testing experiences and professional analysis, not vendor relationships or promotional considerations.
Related Articles
More from Business Software

Microsoft 365 Backup: Why You Need It and Best Options (2026)
Microsoft's native retention isn't backup. Compare iDrive M365, Veeam, and Acronis for business backup. Includes employee deletion recovery walkthrough and pricing.
22 min read

iDrive vs Acronis Cyber Protect 2026: Affordable Backup vs All-in-One Security
We compare iDrive Business and Acronis Cyber Protect for small business backup. Head-to-head on pricing, backup features, security capabilities, compliance, and management.
16 min read

iDrive vs Backblaze Business 2026: Which Cloud Backup Is Right for Your Team?
Head-to-head comparison of iDrive and Backblaze for business cloud backup. We compare pricing for 5-50 users, server backup, compliance, recovery options, and ease of use.
17 min read
